
|
|
Advertisements:
EconomyEconomy - overview
High population density and Israeli security controls placed on the Gaza Strip since the end of the second intifada have degraded economic conditions in this territory, which is smaller than the West Bank. Israeli-imposed border closures, which became more restrictive after HAMAS seized control of the territory in June 2007, have resulted in high unemployment, elevated poverty rates, and the near collapse of the private sector that had relied on export markets. The population is reliant on large-scale humanitarian assistance - led by UN agencies. Changes to Israeli restrictions on imports in 2010 resulted in a rebound in some economic activity, but regular exports from Gaza still are not permitted. Gdp (purchasing power parity)
See entry for West Bank
Gdp - real growth rate
See entry for West Bank
Gdp - per capita (ppp)
See entry for West Bank
Gdp - composition by sector
See entry for West Bank
Labor force World Ranking: 161
348,200 (2010)
Labor force - by occupation
Agriculture 5.1%
Industry 15.6% Services 79.3% (2010 est.) Unemployment rate World Ranking: 184
40% (2010 est.)
40% (2009 est.) Population below poverty line
38% (2010 est.)
Budget
See entry for West Bank
Inflation rate (consumer prices) World Ranking: 123
5% (2011 est.)
6% (2010 est.) Note Includes West Bank Commercial bank prime lending rate
See entry for West Bank
Stock of broad money World Ranking: 117
$6.674 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $6.674 billionStock of domestic credit World Ranking: 148
$1.503 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $1.353 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Agriculture - products
Olives, fruit, vegetables, flowers; beef, dairy products Industries
Textiles, food processing, furniture Industrial production growth rate
See entry for West Bank
Electricity - production World Ranking: 213
51,000 kWh (2011 est.)
Electricity - consumption World Ranking: 214
202,000 kWh (2009)
Electricity - exports
0 kWh (2011 est.)
Electricity - imports
193,000 kWh (2011 est.)
Oil - production
See entry for West Bank
Oil - consumption
See entry for West Bank
Oil - exports
See entry for West Bank
Oil - imports
See entry for West Bank
Oil - proved reserves World Ranking: 134
0 bbl (1 January 2010 est.)
Exports - commodities
Strawberries, carnations, vegetables Imports
See entry for West Bank
Imports - commodities
Food, consumer goods
Note Israel permits limited imports through crossings with Gaza, but many "dual use" goods, such as construction materials, are smuggled through tunnels beneath Gaza's border with Egypt Debt - external
See entry for West Bank
Exchange rates
New Israeli shekels (ILS) per US dollar - 3.5781 (2011)3.739 (2010 est.) 3.9323 (2009) 3.56 (2008) 4.14 (2007) Fiscal year
Calendar year
Comments
Add a new comment: |
Advertisement
Members area
Gaza Strip:
GPS points from Gaza Strip
|
||||||||
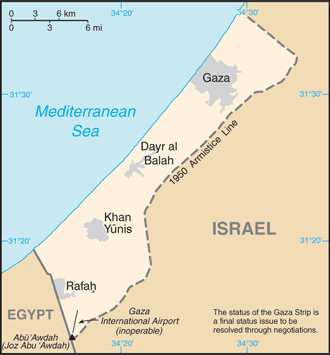
 The September 1993 Israel-PLO Declaration of Principles on Interim Self-Government Arrangements provided for a transitional period of Palestinian self-rule in the West Bank and Gaza Strip. Under a series of agreements signed between May 1994 and September 1999, Israel transferred to the Palestinian Authority (PA) security and civilian responsibility for many Palestinian-populated areas of the West Bank and Gaza Strip. Negotiations to determine the permanent status of the West Bank and Gaza Strip stalled following the outbreak of an intifada in September 2000. In April 2003, the Quartet (US, EU, UN, and Russia) presented a roadmap to a final settlement of the conflict by 2005 based on reciprocal steps by the two parties leading to two states, Israel and a democratic Palestine. Following Palestinian leader Yasir ARAFAT's death in late 2004, Mahmud ABBAS was elected PA president in January 2005. A month later, Israel and the PA agreed to the Sharm el-Sheikh Commitments in an effort to move the peace process forward. In September 2005, Israel unilaterally withdrew all of its settlers and soldiers and dismantled its military facilities in the Gaza Strip and withdrew settlers and redeployed soldiers from four small northern West Bank settlements. Nonetheless, Israel still controls maritime, airspace, and other access to the Gaza Strip; Israel also enforces a restricted zone along the border inside Gaza. In January 2006, the Islamic Resistance Movement, HAMAS, won control of the Palestinian Legislative Council (PLC). HAMAS took control of the PA government in March 2006, but President ABBAS had little success negotiating with HAMAS to present a political platform acceptable to the international community so as to lift economic sanctions on Palestinians. Violent clashes between Fatah and HAMAS supporters in the Gaza Strip in 2006 and early 2007 resulted in numerous Palestinian deaths and injuries. In February 2007, ABBAS and HAMAS Political Bureau Chief Khalid MISHAL signed the Mecca Agreement in Saudi Arabia that resulted in the formation of a Palestinian National Unity Government (NUG) headed by HAMAS member Ismail HANIYA. However, fighting continued in the Gaza Strip, and in June 2007, HAMAS militants succeeded in a violent takeover of all military and governmental institutions in the Gaza Strip. ABBAS that same month dismissed the NUG and through a series of presidential decrees formed a PA government in the West Bank led by independent Salam FAYYAD. Late November 2007 through June 2008 witnessed a substantial increase in Israeli-Palestinian violence. An Egyptian-brokered truce in June 2008 between Israel and HAMAS brought about a five-month pause in hostilities, but spiraling end-of-year violence resulted in the deaths of an estimated 1,100 to 1,400 Palestinians and left tens of thousands of people homeless. International donors pledged $4.5 billion in aid to rebuild the Gaza Strip, but by the end of 2011 large-scale reconstruction had not begun. Fatah and HAMAS in May 2011, under the auspices of Egyptian-sponsored reconciliation negotiations, agreed to reunify the Palestinian territories, but the factions have struggled to finalize details on governing and security structures. The status quo remains with HAMAS in control of the Gaza Strip and ABBAS and the Fatah-dominated PA governing the West Bank.
The September 1993 Israel-PLO Declaration of Principles on Interim Self-Government Arrangements provided for a transitional period of Palestinian self-rule in the West Bank and Gaza Strip. Under a series of agreements signed between May 1994 and September 1999, Israel transferred to the Palestinian Authority (PA) security and civilian responsibility for many Palestinian-populated areas of the West Bank and Gaza Strip. Negotiations to determine the permanent status of the West Bank and Gaza Strip stalled following the outbreak of an intifada in September 2000. In April 2003, the Quartet (US, EU, UN, and Russia) presented a roadmap to a final settlement of the conflict by 2005 based on reciprocal steps by the two parties leading to two states, Israel and a democratic Palestine. Following Palestinian leader Yasir ARAFAT's death in late 2004, Mahmud ABBAS was elected PA president in January 2005. A month later, Israel and the PA agreed to the Sharm el-Sheikh Commitments in an effort to move the peace process forward. In September 2005, Israel unilaterally withdrew all of its settlers and soldiers and dismantled its military facilities in the Gaza Strip and withdrew settlers and redeployed soldiers from four small northern West Bank settlements. Nonetheless, Israel still controls maritime, airspace, and other access to the Gaza Strip; Israel also enforces a restricted zone along the border inside Gaza. In January 2006, the Islamic Resistance Movement, HAMAS, won control of the Palestinian Legislative Council (PLC). HAMAS took control of the PA government in March 2006, but President ABBAS had little success negotiating with HAMAS to present a political platform acceptable to the international community so as to lift economic sanctions on Palestinians. Violent clashes between Fatah and HAMAS supporters in the Gaza Strip in 2006 and early 2007 resulted in numerous Palestinian deaths and injuries. In February 2007, ABBAS and HAMAS Political Bureau Chief Khalid MISHAL signed the Mecca Agreement in Saudi Arabia that resulted in the formation of a Palestinian National Unity Government (NUG) headed by HAMAS member Ismail HANIYA. However, fighting continued in the Gaza Strip, and in June 2007, HAMAS militants succeeded in a violent takeover of all military and governmental institutions in the Gaza Strip. ABBAS that same month dismissed the NUG and through a series of presidential decrees formed a PA government in the West Bank led by independent Salam FAYYAD. Late November 2007 through June 2008 witnessed a substantial increase in Israeli-Palestinian violence. An Egyptian-brokered truce in June 2008 between Israel and HAMAS brought about a five-month pause in hostilities, but spiraling end-of-year violence resulted in the deaths of an estimated 1,100 to 1,400 Palestinians and left tens of thousands of people homeless. International donors pledged $4.5 billion in aid to rebuild the Gaza Strip, but by the end of 2011 large-scale reconstruction had not begun. Fatah and HAMAS in May 2011, under the auspices of Egyptian-sponsored reconciliation negotiations, agreed to reunify the Palestinian territories, but the factions have struggled to finalize details on governing and security structures. The status quo remains with HAMAS in control of the Gaza Strip and ABBAS and the Fatah-dominated PA governing the West Bank.