
|
|
Advertisements:
EconomyEconomy - overview
Hungary has made the transition from a centrally planned to a market economy, with a per capita income nearly two-thirds that of the EU-25 average. The private sector accounts for more than 80% of GDP. Foreign ownership of and investment in Hungarian firms are widespread, with cumulative foreign direct investment worth more than $70 billion. In late 2008, Hungary's impending inability to service its short-term debt - brought on by the global financial crisis - led Budapest to obtain an IMF/EU/World Bank-arranged financial assistance package worth over $25 billion. The global economic downturn, declining exports, and low domestic consumption and fixed asset accumulation, dampened by government austerity measures, resulted in an economic contraction of 6.8% in 2009. In 2010 the new government implemented a number of changes including cutting business and personal income taxes, but imposed "crisis taxes" on financial institutions, energy and telecom companies, and retailers. The IMF/EU bail-out program lapsed at the end of the year and was replaced by Post Program Monitoring and Article IV Consultations on overall economic and fiscal processes. The economy began to recover in 2010 with a big boost from exports, especially to Germany, and achieved growth of approximately 1.4% in 2011. At the end of 2011 the government turned to the IMF and the EU to obtain a new loan for foreign currency debt and bond obligations in 2012 and beyond. Whether negotiations result in a loan depend on Hungary meeting EU and IMF requirements for ensuring the independence of monetary, judicial, and data privacy institutions. The EU also launched an Excessive Deficit Procedure and requested that the government outline measures to sustainably reduce the budget deficit to under 3% of GDP. Unemployment remained high, at nearly 11% in 2011. Ongoing economic weakness in Western Europe is likely to further constrain growth in 2012. Gdp (purchasing power parity) World Ranking: 56
$198.1 billion (2011 est.)
$194.8 billion (2010 est.) $192.4 billion (2009 est.) Note Data are in 2011 US dollars Gdp (official exchange rate)
$140.3 billion (2011 est.)
Gdp - real growth rate World Ranking: 159
1.7% (2011 est.)
1.3% (2010 est.) -6.8% (2009 est.) Gdp - per capita (ppp) World Ranking: 63
$19,800 (2011 est.)
$19,500 (2010 est.) $19,200 (2009 est.) Note Data are in 2011 US dollars Gdp - composition by sector
Agriculture 3.7%
Industry 31.3% Services 65% (2011 est.) Labor force World Ranking: 87
4.274 million (2011)
Labor force - by occupation
Agriculture 4.7%
Industry 30.9% Services 64.4% (2010 est.) Unemployment rate World Ranking: 118
10.9% (2011 est.)
11.2% (2010 est.) Population below poverty line
13.9% (2010)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
Lowest 10% 3.1%
Highest 10% 22.6% (2009) Distribution of family income - gini index World Ranking: 134
24.7 (2009)
24.4 (1998) Investment (gross fixed) World Ranking: 130
16.7% of GDP (2011 est.)
Budget
Revenues $74.03 billion
Expenditures $68.16 billion (2011 est.) Taxes and other revenues World Ranking: 14
52.8% of GDP (2011 est.)
Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-) World Ranking: 19
4.2% of GDP
Note In 2011, the Government decided to redirect funds from the country's obligatory private pension scheme into state coffers in order to pay off government debt, effectively renationalizing the private pension system; the 2.9% deficit shown here does not include this change; including this change would result in a budget surplus of 3.6%; the EU launched an Excessive Deficit Procedure against Hungary in January 2012, because it expects the 2013 deficit to reach 3.7%; the primary criticism of Hungary's deficit reductions in 2011 and 2012 was that they were not achieved in a sustainable manner (2011 est.) Public debt World Ranking: 24
80.6% of GDP (2011 est.)
81.3% of GDP (2010 est.) Note General government gross debt is defined in the Maastricht Treaty as consolidated general government gross debt at nominal value, outstanding at the end of the year in the following categories of government liabilities: currency and deposits, securities other than shares excluding financial derivatives, and government, state government, local government, and social security funds. Inflation rate (consumer prices) World Ranking: 96
3.9% (2011 est.)
4.9% (2010 est.) Central bank discount rate World Ranking: 63
7% (31 December 2011)
5.75% (31 December 2010) Commercial bank prime lending rate World Ranking: 125
8.32% (31 December 2011 est.)
7.57% (31 December 2010 est.) Stock of narrow money World Ranking: 59
$30.51 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $31.8 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Stock of broad money World Ranking: 60
$74.5 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $68.78 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Stock of domestic credit World Ranking: 51
$110.2 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $104.8 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Market value of publicly traded shares World Ranking: 60
$18.77 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $27.71 billion (31 December 2010) $28.29 billion (31 December 2009) Agriculture - products
Wheat, corn, sunflower seed, potatoes, sugar beets; pigs, cattle, poultry, dairy products Industries
Mining, metallurgy, construction materials, processed foods, textiles, chemicals (especially pharmaceuticals), motor vehicles Industrial production growth rate World Ranking: 61
5.4% (2011 est.)
Electricity - production World Ranking: 59
37.37 billion kWh (2010 est.)
Electricity - consumption World Ranking: 51
42.57 billion kWh (2010 est.)
Electricity - exports
4.703 billion kWh (2010 est.)
Electricity - imports
9.897 billion kWh (2010 est.)
Oil - production World Ranking: 66
34,480 bbl/day (2010 est.)
Oil - consumption World Ranking: 66
146,600 bbl/day (2010 est.)
Oil - exports World Ranking: 164
0 bbl/day (2011 est.)
Oil - imports World Ranking: 53
171,600 bbl/day (2010 est.)
Oil - proved reserves World Ranking: 84
26.57 million bbl (1 January 2011 est.) Natural gas - production World Ranking: 56
2.494 billion cu m (2010 est.)
Natural gas - consumption World Ranking: 43
12.13 billion cu m (2010 est.)
Natural gas - exports World Ranking: 43
227 million cu m (2010 est.)
Natural gas - imports World Ranking: 25
9.636 billion cu m (2010 est.)
Natural gas - proved reserves World Ranking: 82
8.098 billion cu m (1 January 2011 est.) Current account balance World Ranking: 41
$1.929 billion (2011 est.)
$1.42 billion (2010 est.) Exports World Ranking: 41
$103.1 billion (2011 est.)
$91.45 billion (2010 est.) Exports - commodities
Machinery and equipment 55.3%, other manufactures 30.6%, food products 7.4%, raw materials 3.2%, fuels and electricity 3.3% (2009 est.) Exports - partners
Germany 25.1%, Romania 5.7%, Austria 5.4%, Slovakia 5.4%, Italy 5%, France 4.8%, UK 4.6% (2010 est.) Imports World Ranking: 36
$93.9 billion (2011 est.)
$87.15 billion (2010 est.) Imports - commodities
Machinery and equipment 44.7%, other manufactures 41.3%, fuels and electricity 5.1%, food products, raw materials 6.7% Imports - partners
Germany 24.7%, Russia 8.6%, China 8.4%, Austria 6.2%, Slovakia 4.9%, Poland 4.7%, Netherlands 4.4%, Italy 4.3% (2010 est.) Reserves of foreign exchange and gold World Ranking: 38
$48.84 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $44.99 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Debt - external World Ranking: 33
$184.5 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $178.9 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Stock of direct foreign investment - at home World Ranking: 47
$71.89 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $69.46 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad World Ranking: 42
$20.56 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $19.59 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Exchange rates
Forints (HUF) per US dollar -
201.06 (2011 est.) 207.94 (2010 est.) 202.34 (2009) 171.8 (2008) 183.83 (2007) Fiscal year
Calendar year
Comments
Add a new comment: |
Advertisement
Members area
Hungary (Budapest):
GPS points from Hungary (Budapest)
|
||||||||
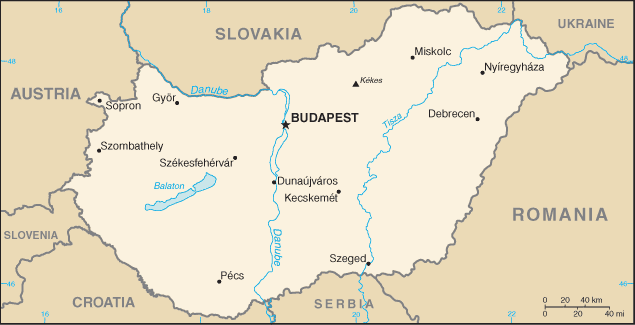
 Hungary became a Christian kingdom in A.D. 1000 and for many centuries served as a bulwark against Ottoman Turkish expansion in Europe. The kingdom eventually became part of the polyglot Austro-Hungarian Empire, which collapsed during World War I. The country fell under Communist rule following World War II. In 1956, a revolt and an announced withdrawal from the Warsaw Pact were met with a massive military intervention by Moscow. Under the leadership of Janos KADAR in 1968, Hungary began liberalizing its economy, introducing so-called "Goulash Communism." Hungary held its first multiparty elections in 1990 and initiated a free market economy. It joined NATO in 1999 and the EU five years later. In 2011, Hungary assumed the six-month rotating presidency of the EU for the first time.
Hungary became a Christian kingdom in A.D. 1000 and for many centuries served as a bulwark against Ottoman Turkish expansion in Europe. The kingdom eventually became part of the polyglot Austro-Hungarian Empire, which collapsed during World War I. The country fell under Communist rule following World War II. In 1956, a revolt and an announced withdrawal from the Warsaw Pact were met with a massive military intervention by Moscow. Under the leadership of Janos KADAR in 1968, Hungary began liberalizing its economy, introducing so-called "Goulash Communism." Hungary held its first multiparty elections in 1990 and initiated a free market economy. It joined NATO in 1999 and the EU five years later. In 2011, Hungary assumed the six-month rotating presidency of the EU for the first time.