
|
|
Advertisements:
EconomyEconomy - overview
Morocco has capitalized on its proximity to Europe and relatively low labor costs to build a diverse, open, market-oriented economy. In the 1980s Morocco pursued austerity measures and pro-market reforms, overseen by the IMF. Since taking the throne in 1999, King MOHAMMED VI has presided over a stable economy marked by steady growth, low inflation, and generally declining government debt. Industrial development strategies and infrastructure improvements - most visibly illustrated by a new port and free trade zone near Tangier - are improving Morocco's competitiveness. Key sectors of the economy include agriculture, tourism, phosphates, textiles, apparel, and subcomponents. In 2006 Morocco entered into a bilateral Free Trade Agreement with the United States; it remains the only African country to have one. In 2008 Morocco entered into an Advanced Status agreement with the European Union. Despite Morocco's economic progress, the country suffers from high unemployment and poverty. In 2011, high food and fuel prices strained the government's budget and widened the country's current account deficit. Key economic challenges for Morocco include fighting corruption, reducing government spending, reforming the education system and judiciary, addressing socioeconomic disparities, and building more diverse, higher value-added industries. Gdp (purchasing power parity) World Ranking: 59
$164.7 billion (2011 est.)
$157.9 billion (2010 est.) $152.3 billion (2009 est.) Note Data are in 2011 US dollars Gdp (official exchange rate)
$99.24 billion (2011 est.)
Gdp - real growth rate World Ranking: 86
4.3% (2011 est.)
3.7% (2010 est.) 4.9% (2009 est.) Gdp - per capita (ppp) World Ranking: 149
$5,100 (2011 est.)
$5,000 (2010 est.) $4,800 (2009 est.) Note Data are in 2011 US dollars Gdp - composition by sector
Agriculture 16.6%
Industry 32.2% Services 51.2% (2011 est.) Labor force World Ranking: 46
11.54 million (2011 est.)
Labor force - by occupation
Agriculture 44.6%
Industry 19.8% Services 35.5% (2006 est.) Unemployment rate World Ranking: 102
8.9% (2011 est.)
9.1% (2010 est.) Population below poverty line
15% (2007 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
Lowest 10% 2.7%
Highest 10% 33.2% (2007) Distribution of family income - gini index World Ranking: 55
40.9 (2007 est.)
39.5 (1999 est.) Investment (gross fixed) World Ranking: 18
30.8% of GDP (2011 est.)
Budget
Revenues $25.69 billion
Expenditures $31.38 billion (2011 est.) Taxes and other revenues World Ranking: 119
25.9% of GDP (2011 est.)
Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-) World Ranking: 170
-5.7% of GDP (2011 est.)
Public debt World Ranking: 39
64% of GDP (2011 est.)
61.1% of GDP (2010 est.) Inflation rate (consumer prices) World Ranking: 14
1.4% (2011 est.)
1% (2010 est.) Central bank discount rate World Ranking: 98
6.5% (31 December 2010 est.)
3.31% (31 December 2009 est.) Commercial bank prime lending rate World Ranking: 138
6.5% (31 December 2011 est.)
6.3% (31 December 2010 est.) Stock of narrow money World Ranking: 42
$64.75 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $66.1 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Stock of broad money World Ranking: 53
$107.2 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $109.8 billion (31 December 2009 est.) Stock of domestic credit World Ranking: 53
$94.01 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $88.84 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Market value of publicly traded shares World Ranking: 49
$60.09 billion (31 December 2011) $69.15 billion (31 December 2010) $62.91 billion (31 December 2009) Agriculture - products
Barley, wheat, citrus fruits, grapes, vegetables, olives; livestock; wine Industries
Phosphate rock mining and processing, food processing, leather goods, textiles, construction, energy, tourism Industrial production growth rate World Ranking: 75
4.4% (2010 est.)
Electricity - production World Ranking: 71
19.49 billion kWh (2008 est.)
Electricity - consumption World Ranking: 67
21.47 billion kWh (2008 est.)
Electricity - exports
0 kWh (2009 est.)
Electricity - imports
3.429 billion kWh (2009 est.)
Oil - production World Ranking: 100
3,938 bbl/day (2010 est.)
Oil - consumption World Ranking: 55
209,000 bbl/day (2010 est.)
Oil - exports World Ranking: 85
25,090 bbl/day (2009 est.)
Oil - imports World Ranking: 45
221,000 bbl/day (2009 est.)
Oil - proved reserves World Ranking: 98
680,000 bbl (1 January 2011 est.) Natural gas - production World Ranking: 81
60 million cu m (2009 est.)
Natural gas - consumption World Ranking: 96
560 million cu m (2009 est.)
Natural gas - exports World Ranking: 148
0 cu m (2009 est.)
Natural gas - imports World Ranking: 67
500 million cu m (2009 est.)
Natural gas - proved reserves World Ranking: 97
1.444 billion cu m (1 January 2011 est.) Current account balance World Ranking: 174
-$8.868 billion (2011 est.)
-$4.209 billion (2010 est.) Exports World Ranking: 72
$20.99 billion (2011 est.)
$17.58 billion (2010 est.) Exports - commodities
Clothing and textiles, electric components, inorganic chemicals, transistors, crude minerals, fertilizers (including phosphates), petroleum products, citrus fruits, vegetables, fish Exports - partners
Spain 18.6%, France 16.9%, Brazil 6%, US 4.8%, India 4.5% (2011) Imports World Ranking: 59
$40.39 billion (2011 est.)
$32.65 billion (2010 est.) Imports - commodities
Crude petroleum, textile fabric, telecommunications equipment, wheat, gas and electricity, transistors, plastics Imports - partners
France 15.4%, Spain 14.4%, China 7.7%, US 7.3%, Saudi Arabia 6.1%, Italy 5.1%, Germany 4.8% (2011) Reserves of foreign exchange and gold World Ranking: 57
$20.65 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $23.61 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Debt - external World Ranking: 72
$28.08 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $26.58 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Stock of direct foreign investment - at home World Ranking: 56
$46.43 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $45.26 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad World Ranking: 72
$1.329 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $1.851 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Exchange rates
Moroccan dirhams (MAD) per US dollar - 8.0899 (2011 est.)8.4172 (2010 est.) 8.0571 (2009) 7.526 (2008) 8.3563 (2007) Fiscal year
Calendar year
Comments
Add a new comment: |
Advertisement
Members area
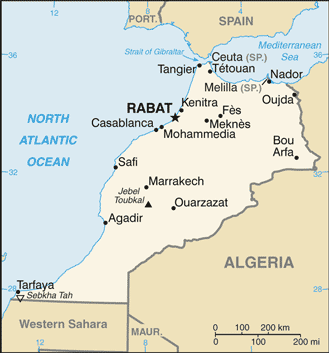
Morocco (Rabat):
GPS points from Morocco (Rabat)
|
||||||||
 In 788, about a century after the Arab conquest of North Africa, a series of Moroccan Muslim dynasties began to rule in Morocco. In the 16th century, the Sa'adi monarchy, particularly under Ahmad AL-MANSUR (1578-1603), repelled foreign invaders and inaugurated a golden age. The Alaouite dynasty, to which the current Moroccan royal family belongs, dates from the 17th century. In 1860, Spain occupied northern Morocco and ushered in a half century of trade rivalry among European powers that saw Morocco's sovereignty steadily erode; in 1912, the French imposed a protectorate over the country. A protracted independence struggle with France ended successfully in 1956. The internationalized city of Tangier and most Spanish possessions were turned over to the new country that same year. Sultan MOHAMMED V, the current monarch's grandfather, organized the new state as a constitutional monarchy and in 1957 assumed the title of king. Morocco annexed Western Sahara during the late 1970s, but final resolution on the status of the territory remains unresolved. Gradual political reforms in the 1990s resulted in the establishment of a bicameral legislature, which first met in 1997. Under King MOHAMMED VI - who in 1999 succeeded his father to the throne - human rights have improved. Morocco enjoys a moderately free press, but the government has taken action against journalists who they perceive to be challenging the monarchy, Islam, and the status of Western Sahara. Influenced by protests elsewhere in the Middle East and North Africa, in February 2011 thousands of Moroccans began weekly rallies in multiple cities across the country to demand greater democracy and a crackdown on government corruption. Police response to most of the protests was subdued compared to the violence elsewhere in the region. A commission set up in March 2011 presented a draft constitution that was passed by popular referendum in July 2011. Under the new constitution, some new powers were extended to parliament and the prime minister, but ultimate authority remained in the hands of the monarch. That same month, the king urged swift implementation of the new constitution, starting with the holding of parliamentary elections in 2011 instead of in 2012. A prominent moderate Islamist party, the Justice and Development Party, subsequently won the largest number of seats on 25 November 2011, becoming the first Islamist party to lead the Moroccan Government. In January 2012, Morocco assumed a nonpermanent seat on the UN Security Council for the 2012-13 term.
In 788, about a century after the Arab conquest of North Africa, a series of Moroccan Muslim dynasties began to rule in Morocco. In the 16th century, the Sa'adi monarchy, particularly under Ahmad AL-MANSUR (1578-1603), repelled foreign invaders and inaugurated a golden age. The Alaouite dynasty, to which the current Moroccan royal family belongs, dates from the 17th century. In 1860, Spain occupied northern Morocco and ushered in a half century of trade rivalry among European powers that saw Morocco's sovereignty steadily erode; in 1912, the French imposed a protectorate over the country. A protracted independence struggle with France ended successfully in 1956. The internationalized city of Tangier and most Spanish possessions were turned over to the new country that same year. Sultan MOHAMMED V, the current monarch's grandfather, organized the new state as a constitutional monarchy and in 1957 assumed the title of king. Morocco annexed Western Sahara during the late 1970s, but final resolution on the status of the territory remains unresolved. Gradual political reforms in the 1990s resulted in the establishment of a bicameral legislature, which first met in 1997. Under King MOHAMMED VI - who in 1999 succeeded his father to the throne - human rights have improved. Morocco enjoys a moderately free press, but the government has taken action against journalists who they perceive to be challenging the monarchy, Islam, and the status of Western Sahara. Influenced by protests elsewhere in the Middle East and North Africa, in February 2011 thousands of Moroccans began weekly rallies in multiple cities across the country to demand greater democracy and a crackdown on government corruption. Police response to most of the protests was subdued compared to the violence elsewhere in the region. A commission set up in March 2011 presented a draft constitution that was passed by popular referendum in July 2011. Under the new constitution, some new powers were extended to parliament and the prime minister, but ultimate authority remained in the hands of the monarch. That same month, the king urged swift implementation of the new constitution, starting with the holding of parliamentary elections in 2011 instead of in 2012. A prominent moderate Islamist party, the Justice and Development Party, subsequently won the largest number of seats on 25 November 2011, becoming the first Islamist party to lead the Moroccan Government. In January 2012, Morocco assumed a nonpermanent seat on the UN Security Council for the 2012-13 term.