
|
|
Advertisements:
GeographyLocation
Southern South America, bordering the South Pacific Ocean, between Argentina and Peru Geographic coordinates
30 00 S, 71 00 W
Map references
South America
Area World Ranking: 38
Total 756,102 sq km
Land 743,812 sq km Water 12,290 sq km Note Includes Easter Island (Isla de Pascua) and Isla Sala y Gomez Area - comparative
Slightly smaller than twice the size of Montana Land boundaries
Total 6,339 km
Border countries Argentina 5,308 km, Bolivia 860 km, Peru 171 km Coastline
6,435 km
Maritime claims
Territorial sea 12 nm
Contiguous zone 24 nm Exclusive economic zone 200 nm Continental shelf 200/350 nm Climate
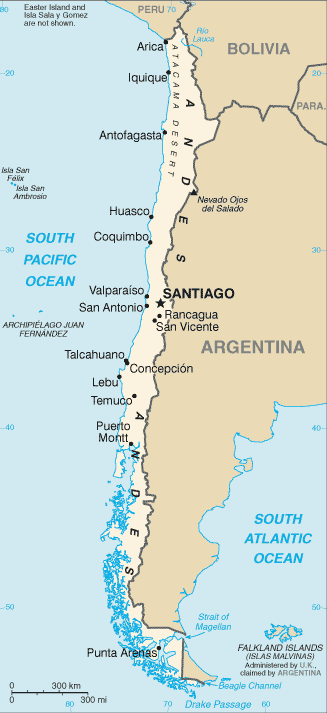
Temperate; desert in north; Mediterranean in central region; cool and damp in south Terrain
Low coastal mountains; fertile central valley; rugged Andes in east Elevation extremes
Lowest point Pacific Ocean 0 m
Highest point Nevado Ojos del Salado 6,880 m Natural resources
Copper, timber, iron ore, nitrates, precious metals, molybdenum, hydropower Land use
Arable land 2.62%
Permanent crops 0.43% Other 96.95% (2005) Irrigated land
19,000 sq km (2003)
Total renewable water resources
922 cu km (2000)
Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural)
Total 12.55 cu km/yr (11%/25%/64%)
Per capita 770 cu m/yr (2000) Natural hazards
Severe earthquakes; active volcanism; tsunamis Volcanism Significant volcanic activity due to more than three-dozen active volcanoes along the Andes Mountains; Lascar (elev. 5,592 m), which last erupted in 2007, is the most active volcano in the northern Chilean Andes; Llaima (elev. 3,125 m) in central Chile, which last erupted in 2009, is another of the country's most active; Chaiten's 2008 eruption forced major evacuations; other notable historically active volcanoes include Cerro Hudson, Copahue, Guallatiri, Llullaillaco, Nevados de Chillan, Puyehue, San Pedro, and Villarrica Environment - current issues
Widespread deforestation and mining threaten natural resources; air pollution from industrial and vehicle emissions; water pollution from raw sewage Environment - international agreements
Party to
Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling Signed, but not ratified None of the selected agreements Geography - note
The longest north-south trending country in the world, extending across 38 degrees of latitude; strategic location relative to sea lanes between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans (Strait of Magellan, Beagle Channel, Drake Passage); Atacama Desert - the driest desert in the world - spreads across the northern part of the country; the crater lake of Ojos del Salado is the world's highest lake (at 6,390 m)
Comments
Add a new comment: |
Advertisement
Members area
Chile (Santiago):
GPS points from Chile (Santiago)
|
||||||||
 Prior to the arrival of the Spanish in the 16th century, the Inca ruled northern Chile while the indigenous Mapuche inhabited central and southern Chile. Although Chile declared its independence in 1810, decisive victory over the Spanish was not achieved until 1818. In the War of the Pacific (1879-83), Chile defeated Peru and Bolivia and won its present northern regions. It was not until the 1880s that the Mapuche Indians were completely subjugated. After a series of elected governments, the three-year-old Marxist government of Salvador ALLENDE was overthrown in 1973 by a military coup led by Augusto PINOCHET, who ruled until a freely elected president was installed in 1990. Sound economic policies, maintained consistently since the 1980s, have contributed to steady growth, reduced poverty rates by over half, and have helped secure the country's commitment to democratic and representative government. Chile has increasingly assumed regional and international leadership roles befitting its status as a stable, democratic nation.
Prior to the arrival of the Spanish in the 16th century, the Inca ruled northern Chile while the indigenous Mapuche inhabited central and southern Chile. Although Chile declared its independence in 1810, decisive victory over the Spanish was not achieved until 1818. In the War of the Pacific (1879-83), Chile defeated Peru and Bolivia and won its present northern regions. It was not until the 1880s that the Mapuche Indians were completely subjugated. After a series of elected governments, the three-year-old Marxist government of Salvador ALLENDE was overthrown in 1973 by a military coup led by Augusto PINOCHET, who ruled until a freely elected president was installed in 1990. Sound economic policies, maintained consistently since the 1980s, have contributed to steady growth, reduced poverty rates by over half, and have helped secure the country's commitment to democratic and representative government. Chile has increasingly assumed regional and international leadership roles befitting its status as a stable, democratic nation.