|
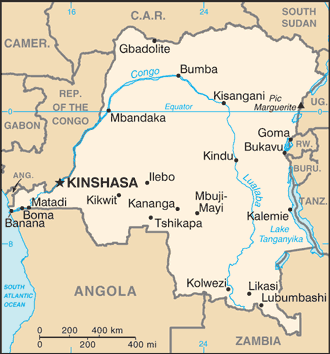
Administrative divisions (GPS Maps)
Geography
People and Society
Government
Economy
Communications
Transportation
Military |
 |
 Established as a Belgian colony in 1908, the then-Republic of the Congo gained its independence in 1960, but its early years were marred by political and social instability. Col. Joseph MOBUTU seized power and declared himself president in a November 1965 coup. He subsequently changed his name - to MOBUTU Sese Seko - as well as that of the country - to Zaire. MOBUTU retained his position for 32 years through several sham elections, as well as through brutal force. Ethnic strife and civil war, touched off by a massive inflow of refugees in 1994 from fighting in Rwanda and Burundi, led in May 1997 to the toppling of the MOBUTU regime by a rebellion backed by Rwanda and Uganda and fronted by Laurent KABILA. He renamed the country the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), but in August 1998 his regime was itself challenged by a second insurrection again backed by Rwanda and Uganda. Troops from Angola, Chad, Namibia, Sudan, and Zimbabwe intervened to support KABILA's regime. A cease-fire was signed in July 1999 by the DRC, Congolese armed rebel groups, Angola, Namibia, Rwanda, Uganda, and Zimbabwe but sporadic fighting continued. Laurent KABILA was assassinated in January 2001 and his son, Joseph KABILA, was named head of state. In October 2002, the new president was successful in negotiating the withdrawal of Rwandan forces occupying eastern Congo; two months later, the Pretoria Accord was signed by all remaining warring parties to end the fighting and establish a government of national unity. A transitional government was set up in July 2003; it held a successful constitutional referendum in December 2005 and elections for the presidency, National Assembly, and provincial legislatures took place in 2006. In the most recent national elections, held in November 2011, disputed results allowed Joseph KABILA to be reelected to the presidency . Established as a Belgian colony in 1908, the then-Republic of the Congo gained its independence in 1960, but its early years were marred by political and social instability. Col. Joseph MOBUTU seized power and declared himself president in a November 1965 coup. He subsequently changed his name - to MOBUTU Sese Seko - as well as that of the country - to Zaire. MOBUTU retained his position for 32 years through several sham elections, as well as through brutal force. Ethnic strife and civil war, touched off by a massive inflow of refugees in 1994 from fighting in Rwanda and Burundi, led in May 1997 to the toppling of the MOBUTU regime by a rebellion backed by Rwanda and Uganda and fronted by Laurent KABILA. He renamed the country the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), but in August 1998 his regime was itself challenged by a second insurrection again backed by Rwanda and Uganda. Troops from Angola, Chad, Namibia, Sudan, and Zimbabwe intervened to support KABILA's regime. A cease-fire was signed in July 1999 by the DRC, Congolese armed rebel groups, Angola, Namibia, Rwanda, Uganda, and Zimbabwe but sporadic fighting continued. Laurent KABILA was assassinated in January 2001 and his son, Joseph KABILA, was named head of state. In October 2002, the new president was successful in negotiating the withdrawal of Rwandan forces occupying eastern Congo; two months later, the Pretoria Accord was signed by all remaining warring parties to end the fighting and establish a government of national unity. A transitional government was set up in July 2003; it held a successful constitutional referendum in December 2005 and elections for the presidency, National Assembly, and provincial legislatures took place in 2006. In the most recent national elections, held in November 2011, disputed results allowed Joseph KABILA to be reelected to the presidency . |
|
Advertisements
|
Advertisements
|
Telephones - main lines in use World Ranking: 166
42,000 (2011)
Telephones - mobile cellular World Ranking: 52
15.673 million (2011)
Telephone system
General assessment Barely adequate wire and microwave radio relay service in and between urban areas; domestic satellite system with 14 earth stations; inadequate fixed line infrastructure Domestic State-owned operator providing less than 1 fixed-line connection per 1000 persons; given the backdrop of a wholly inadequate fixed-line infrastructure, the use of mobile-cellular services has surged and mobile teledensity is roughly 20 per 100 persons International Country code - 243; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2011)
Broadcast media
State-owned TV broadcast station with near national coverage; more than a dozen privately-owned TV stations with 2 having near national coverage; 2 state-owned radio stations are supplemented by more than 100 private radio stations; transmissions of at least 2 international broadcasters are available (2007)
Internet country code
.cd
Internet hosts World Ranking: 159
2,514 (2010)
Internet users World Ranking: 132
290,000 (2008)
--- There are no comments yet ---
Add a new comment:
|
Advertisement
Members area
Democratic Republic Of The Congo (Kinshasa):
GPS points from Democratic Republic Of The Congo (Kinshasa)
 Lubala Democratic Republic Of The Congo (general)
Lubala Democratic Republic Of The Congo (general)
 Wangi Province De L' Equateur
Wangi Province De L' Equateur
 Banga-melo Democratic Republic Of The Congo (general)
Banga-melo Democratic Republic Of The Congo (general)
|



 Established as a Belgian colony in 1908, the then-Republic of the Congo gained its independence in 1960, but its early years were marred by political and social instability. Col. Joseph MOBUTU seized power and declared himself president in a November 1965 coup. He subsequently changed his name - to MOBUTU Sese Seko - as well as that of the country - to Zaire. MOBUTU retained his position for 32 years through several sham elections, as well as through brutal force. Ethnic strife and civil war, touched off by a massive inflow of refugees in 1994 from fighting in Rwanda and Burundi, led in May 1997 to the toppling of the MOBUTU regime by a rebellion backed by Rwanda and Uganda and fronted by Laurent KABILA. He renamed the country the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), but in August 1998 his regime was itself challenged by a second insurrection again backed by Rwanda and Uganda. Troops from Angola, Chad, Namibia, Sudan, and Zimbabwe intervened to support KABILA's regime. A cease-fire was signed in July 1999 by the DRC, Congolese armed rebel groups, Angola, Namibia, Rwanda, Uganda, and Zimbabwe but sporadic fighting continued. Laurent KABILA was assassinated in January 2001 and his son, Joseph KABILA, was named head of state. In October 2002, the new president was successful in negotiating the withdrawal of Rwandan forces occupying eastern Congo; two months later, the Pretoria Accord was signed by all remaining warring parties to end the fighting and establish a government of national unity. A transitional government was set up in July 2003; it held a successful constitutional referendum in December 2005 and elections for the presidency, National Assembly, and provincial legislatures took place in 2006. In the most recent national elections, held in November 2011, disputed results allowed Joseph KABILA to be reelected to the presidency .
Established as a Belgian colony in 1908, the then-Republic of the Congo gained its independence in 1960, but its early years were marred by political and social instability. Col. Joseph MOBUTU seized power and declared himself president in a November 1965 coup. He subsequently changed his name - to MOBUTU Sese Seko - as well as that of the country - to Zaire. MOBUTU retained his position for 32 years through several sham elections, as well as through brutal force. Ethnic strife and civil war, touched off by a massive inflow of refugees in 1994 from fighting in Rwanda and Burundi, led in May 1997 to the toppling of the MOBUTU regime by a rebellion backed by Rwanda and Uganda and fronted by Laurent KABILA. He renamed the country the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), but in August 1998 his regime was itself challenged by a second insurrection again backed by Rwanda and Uganda. Troops from Angola, Chad, Namibia, Sudan, and Zimbabwe intervened to support KABILA's regime. A cease-fire was signed in July 1999 by the DRC, Congolese armed rebel groups, Angola, Namibia, Rwanda, Uganda, and Zimbabwe but sporadic fighting continued. Laurent KABILA was assassinated in January 2001 and his son, Joseph KABILA, was named head of state. In October 2002, the new president was successful in negotiating the withdrawal of Rwandan forces occupying eastern Congo; two months later, the Pretoria Accord was signed by all remaining warring parties to end the fighting and establish a government of national unity. A transitional government was set up in July 2003; it held a successful constitutional referendum in December 2005 and elections for the presidency, National Assembly, and provincial legislatures took place in 2006. In the most recent national elections, held in November 2011, disputed results allowed Joseph KABILA to be reelected to the presidency .