
|
|
Advertisements:
EconomyEconomy - overview
The German economy - the fifth largest economy in the world in PPP terms and Europe's largest - is a leading exporter of machinery, vehicles, chemicals, and household equipment and benefits from a highly skilled labor force. Like its Western European neighbors, Germany faces significant demographic challenges to sustained long-term growth. Low fertility rates and declining net immigration are increasing pressure on the country's social welfare system and necessitate structural reforms. Reforms launched by the government of Chancellor Gerhard SCHROEDER (1998-2005), deemed necessary to address chronically high unemployment and low average growth, contributed to strong growth in 2006 and 2007 and falling unemployment. These advances, as well as a government subsidized, reduced working hour scheme, help explain the relatively modest increase in unemployment during the 2008-09 recession - the deepest since World War II - and its decrease to 6.0% in 2011. GDP contracted 5.1% in 2009 but grew by 3.6% in 2010, and 2.7% in 2011. The recovery was attributable primarily to rebounding manufacturing orders and exports - increasingly outside the Euro Zone. Germany's central bank projects that GDP will grow 0.6% in 2012, a reflection of the worsening euro-zone financial crisis and the financial burden it places on Germany as well as falling demand for German exports. Domestic demand is therefore becoming a more significant driver of Germany's economic expansion. Stimulus and stabilization efforts initiated in 2008 and 2009 and tax cuts introduced in Chancellor Angela MERKEL's second term increased Germany's budget deficit to 3.3% in 2010, but slower spending and higher tax revenues reduce the deficit to 1.7% in 2011, below the EU's 3% limit. A constitutional amendment approved in 2009 limits the federal government to structural deficits of no more than 0.35% of GDP per annum as of 2016. Following the March 2011 Fukushima nuclear disaster, Chancellor Angela Merkel announced in May 2011 that eight of the country's 17 nuclear reactors would be shut down immediately and the remaining plants would close by 2022. Germany hopes to replace nuclear power with renewable energy. Before the shutdown of the eight reactors, Germany relied on nuclear power for 23% of its energy and 46% of its base-load electrical production. Gdp (purchasing power parity) World Ranking: 6
$3.139 trillion (2011 est.)
$3.046 trillion (2010 est.) $2.941 trillion (2009 est.) Note Data are in 2011 US dollars Gdp (official exchange rate)
$3.577 trillion (2011 est.)
Gdp - real growth rate World Ranking: 116
3.1% (2011 est.)
3.6% (2010 est.) -5.1% (2009 est.) Gdp - per capita (ppp) World Ranking: 26
$38,400 (2011 est.)
$37,300 (2010 est.) $35,900 (2009 est.) Note Data are in 2011 US dollars Gdp - composition by sector
Agriculture 0.8%
Industry 28.6% Services 70.6% (2011 est.) Labor force World Ranking: 14
43.62 million (2011 est.)
Labor force - by occupation
Agriculture 1.6%
Industry 24.6% Services 73.8% (2011) Unemployment rate World Ranking: 65
6% (2011 est.)
7.1% (2010 est.) Note This is the International Labor Organization's rate for international comparisons; Germany's Federal Employment Agency reported an annual average unemployment rate of 7.1% for 2011 and 7.7% for 2010. Population below poverty line
15.5% (2010 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
Lowest 10% 3.6%
Highest 10% 24% (2000) Distribution of family income - gini index World Ranking: 124
27 (2006)
30 (1994) Investment (gross fixed) World Ranking: 116
18.2% of GDP (2011 est.)
Budget
Revenues $1.551 trillion
Expenditures $1.588 trillion (2011 est.) Taxes and other revenues World Ranking: 33
43.4% of GDP (2011 est.)
Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-) World Ranking: 61
-1% of GDP (2011 est.)
Public debt World Ranking: 23
81.8% of GDP (2011 est.)
83.4% of GDP (2010 est.) Note General government gross debt is defined in the Maastricht Treaty as consolidated general government gross debt at nominal value, outstanding at the end of the year in the following categories of government liabilities (as defined in ESA95): currency and deposits (AF.2), securities other than shares excluding financial derivatives (AF.3, excluding AF.34), and loans (AF.4); the general government sector comprises the sub-sectors of central government, state government, local government and social security funds; the series are presented as a percentage of GDP and in millions of euro; GDP used as a denominator is the gross domestic product at current market prices; data expressed in national currency are converted into euro using end-year exchange rates provided by the European Central Bank Inflation rate (consumer prices) World Ranking: 36
2.3% (2011 est.)
1.1% (2010 est.) Central bank discount rate World Ranking: 114
1.75% (31 December 2011)
1.75% (31 December 2010) Note This is the European Central Bank's rate on the marginal lending facility, which offers overnight credit to banks in the euro area Commercial bank prime lending rate World Ranking: 157
8.4% (31 December 2011 est.)
4.96% (31 December 2009 est.) Stock of narrow money World Ranking: 5
$1.777 trillion (31 December 2011 est.) $1.747 trillion (31 December 2010 est.) Note See entry for the European Union for money supply in the euro area; the European Central Bank (ECB) controls monetary policy for the 17 members of the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU); individual members of the EMU do not control the quantity of money circulating within their own borders Stock of broad money World Ranking: 5
$4.278 trillion (31 December 2011 est.) $4.173 trillion (31 December 2010 est.) Stock of domestic credit World Ranking: 6
$4.689 trillion (31 December 2011 est.) $5.2 trillion (31 December 2009 est.) Market value of publicly traded shares World Ranking: 12
$1.184 trillion (31 December 2011) $1.43 trillion (31 December 2010) $1.298 trillion (31 December 2009) Agriculture - products
Potatoes, wheat, barley, sugar beets, fruit, cabbages; cattle, pigs, poultry Industries
Among the world's largest and most technologically advanced producers of iron, steel, coal, cement, chemicals, machinery, vehicles, machine tools, electronics, food and beverages, shipbuilding, textiles Industrial production growth rate World Ranking: 26
8% (2011 est.)
Electricity - production World Ranking: 7
556.4 billion kWh (2009 est.)
Electricity - consumption World Ranking: 8
544.5 billion kWh (2008 est.)
Electricity - exports
54.13 billion kWh (2009 est.)
Electricity - imports
12.28 billion kWh (2009 est.)
Oil - production World Ranking: 46
147,200 bbl/day (2010 est.)
Oil - consumption World Ranking: 7
2.495 million bbl/day (2010 est.) Oil - exports World Ranking: 31
470,200 bbl/day (2009 est.)
Oil - imports World Ranking: 6
2.671 million bbl/day (2009 est.) Oil - proved reserves World Ranking: 57
276 million bbl (1 January 2011 est.) Natural gas - production World Ranking: 37
12.65 billion cu m (2010 est.)
Natural gas - consumption World Ranking: 7
99.5 billion cu m (2010 est.)
Natural gas - exports World Ranking: 15
16.19 billion cu m (2010 est.)
Natural gas - imports World Ranking: 3
99.63 billion cu m (2010 est.)
Natural gas - proved reserves World Ranking: 49
175.6 billion cu m (1 January 2011 est.) Current account balance World Ranking: 2
$188.6 billion (2011 est.)
$187.9 billion (2010 est.) Exports World Ranking: 4
$1.408 trillion (2011 est.)
$1.303 trillion (2010 est.) Exports - commodities
Motor vehicles, machinery, chemicals, computer and electronic products, electrical equipment, pharmaceuticals, metals, transport equipment, foodstuffs, textiles, rubber and plastic products Exports - partners
France 9.4%, US 6.8%, Netherlands 6.6%, UK 6.2%, Italy 6.2%, China 5.7%, Austria 5.5%, Belgium 4.7%, Switzerland 4.4% (2009 est.) Imports World Ranking: 4
$1.198 trillion (2011 est.)
$1.099 trillion (2010 est.) Imports - commodities
Machinery, data processing equipment, vehicles, chemicals, oil and gas, metals, electric equipment, pharmaceuticals, foodstuffs, agricultural products Imports - partners
China 9.7%, Netherlands 8.4%, France 7.6%, US 5.7%, Italy 5.2%, UK 4.7%, Belgium 4.2%, Austria 4.1%, Switzerland 4.1% (2009 est.) Reserves of foreign exchange and gold World Ranking: 12
$238.9 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $216.5 billionDebt - external World Ranking: 5
$5.624 trillion (30 June 2011)
$4.713 trillion (30 June 2010) Stock of direct foreign investment - at home World Ranking: 6
$940.1 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $910.4 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad World Ranking: 4
$1.465 trillion (31 December 2011 est.) $1.406 trillion (31 December 2010 est.) Exchange rates
Euros (EUR) per US dollar -
0.7194 (2011 est.) 0.755 (2010 est.) 0.7198 (2009 est.) 0.6827 (2008 est.) 0.7345 (2007 est.) Fiscal year
Calendar year
Comments
Add a new comment: |
Advertisement
Members area
Germany (Berlin):
 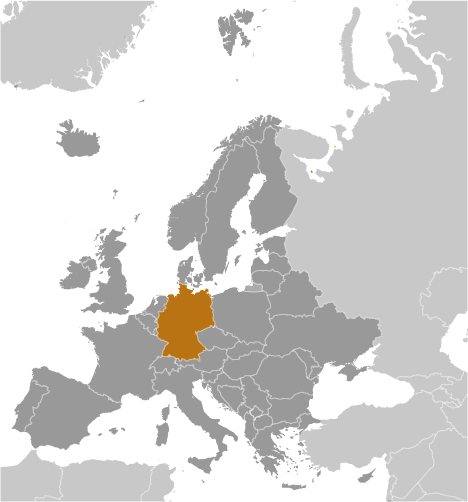
GPS points from Germany (Berlin)
|
||||||||
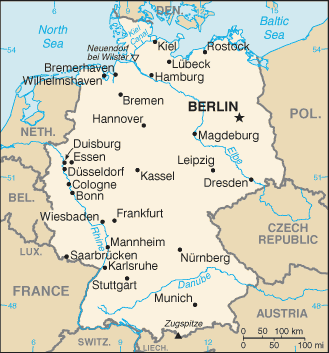
 As Europe's largest economy and second most populous nation (after Russia), Germany is a key member of the continent's economic, political, and defense organizations. European power struggles immersed Germany in two devastating World Wars in the first half of the 20th century and left the country occupied by the victorious Allied powers of the US, UK, France, and the Soviet Union in 1945. With the advent of the Cold War, two German states were formed in 1949: the western Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) and the eastern German Democratic Republic (GDR). The democratic FRG embedded itself in key Western economic and security organizations, the EC, which became the EU, and NATO, while the Communist GDR was on the front line of the Soviet-led Warsaw Pact. The decline of the USSR and the end of the Cold War allowed for German unification in 1990. Since then, Germany has expended considerable funds to bring Eastern productivity and wages up to Western standards. In January 1999, Germany and 10 other EU countries introduced a common European exchange currency, the euro. In January 2011, Germany assumed a nonpermanent seat on the UN Security Council for the 2011-12 term.
As Europe's largest economy and second most populous nation (after Russia), Germany is a key member of the continent's economic, political, and defense organizations. European power struggles immersed Germany in two devastating World Wars in the first half of the 20th century and left the country occupied by the victorious Allied powers of the US, UK, France, and the Soviet Union in 1945. With the advent of the Cold War, two German states were formed in 1949: the western Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) and the eastern German Democratic Republic (GDR). The democratic FRG embedded itself in key Western economic and security organizations, the EC, which became the EU, and NATO, while the Communist GDR was on the front line of the Soviet-led Warsaw Pact. The decline of the USSR and the end of the Cold War allowed for German unification in 1990. Since then, Germany has expended considerable funds to bring Eastern productivity and wages up to Western standards. In January 1999, Germany and 10 other EU countries introduced a common European exchange currency, the euro. In January 2011, Germany assumed a nonpermanent seat on the UN Security Council for the 2011-12 term.