
|
|
Advertisements:
EconomyEconomy - overview
Israel has a technologically advanced market economy. It depends on imports of crude oil, grains, raw materials, and military equipment. Cut diamonds, high-technology equipment, and agricultural products (fruits and vegetables) are the leading exports. Israel usually posts sizable trade deficits, which are covered by tourism and other service exports, as well as significant foreign investment inflows. The global financial crisis of 2008-09 spurred a brief recession in Israel, but the country entered the crisis with solid fundamentals - following years of prudent fiscal policy and a resilient banking sector. The economy has recovered better than most advanced, comparably sized economies. In 2010, Israel formally acceded to the OECD. Natural gasfields discovered off Israel's coast during the past two years have brightened Israel's energy security outlook. The Leviathan field was one of the world's largest offshore natural gas finds this past decade. In mid-2011, public protests arose around income inequality and rising housing and commodity prices. The government formed committees to address some of the grievances but has maintained that it will not engage in deficit spending to satisfy populist demands. Gdp (purchasing power parity) World Ranking: 52
$238.2 billion (2011 est.)
$227.5 billion (2010 est.) $217 billion (2009 est.) Note Data are in 2011 US dollars Gdp (official exchange rate)
$242.9 billion (2011 est.)
Gdp - real growth rate World Ranking: 76
4.7% (2011 est.)
4.8% (2010 est.) 0.8% (2009 est.) Gdp - per capita (ppp) World Ranking: 41
$31,400 (2011 est.)
$30,600 (2010 est.) $29,800 (2009 est.) Note Data are in 2011 US dollars Gdp - composition by sector
Agriculture 2.5%
Industry 31.1% Services 64.9% (2011 est.) Labor force World Ranking: 101
3.204 million (2011 est.)
Labor force - by occupation
Agriculture 2%
Industry 16% Services 82% (September 2008) Unemployment rate World Ranking: 58
5.6% (2011 est.)
6.7% (2010 est.) Population below poverty line
23.6%
Note Israel's poverty line is $7.30 per person per day (2007) Household income or consumption by percentage share
Lowest 10% 2.5%
Highest 10% 24.3% (2008) Distribution of family income - gini index World Ranking: 66
39.2 (2008)
35.5 (2001) Investment (gross fixed) World Ranking: 103
19.6% of GDP (2011 est.)
Budget
Revenues $66.68 billion
Expenditures $74.8 billion (2011 est.) Taxes and other revenues World Ranking: 106
27.5% of GDP (2011 est.)
Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-) World Ranking: 109
-3.3% of GDP (2011 est.)
Public debt World Ranking: 31
72.8% of GDP (2011 est.)
74.6% of GDP (2010 est.) Inflation rate (consumer prices) World Ranking: 79
3.5% (2011 est.)
2.7% (2010 est.) Central bank discount rate World Ranking: 110
2.75% (31 December 2011 est.)
2.02% (31 December 2010 est.) Commercial bank prime lending rate World Ranking: 161
5.54% (31 December 2011 est.)
4.492% (31 December 2010 est.) Stock of narrow money World Ranking: 60
$30.21 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $31.29 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Stock of broad money World Ranking: 41
$208.8 billion (31 December 2009 est.) $195.7 billion (31 December 2008 est.) Stock of domestic credit World Ranking: 40
$186.9 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $175.6 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Market value of publicly traded shares World Ranking: 33
$145 billion (31 December 2011) $218.1 billion (31 December 2010) $182.1 billion (31 December 2009) Agriculture - products
Citrus, vegetables, cotton; beef, poultry, dairy products Industries
High-technology products (including aviation, communications, computer-aided design and manufactures, medical electronics, fiber optics), wood and paper products, potash and phosphates, food, beverages, and tobacco, caustic soda, cement, construction, metals products, chemical products, plastics, diamond cutting, textiles, footwear
Industrial production growth rate World Ranking: 123
2% (2011 est.)
Electricity - production World Ranking: 45
53.04 billion kWh (2008 est.)
Electricity - consumption World Ranking: 48
47.16 billion kWh (2008 est.)
Electricity - exports
3.666 billion kWh (2008 est.)
Electricity - imports
NA kWh (2008 est.)
Oil - production World Ranking: 99
4,029 bbl/day (2010 est.)
Oil - consumption World Ranking: 51
238,000 bbl/day (2010 est.)
Oil - exports World Ranking: 65
86,010 bbl/day (2009 est.)
Oil - imports World Ranking: 37
282,200 bbl/day (2009 est.)
Oil - proved reserves World Ranking: 95
1.94 million bbl (1 January 2011 est.) Natural gas - production World Ranking: 60
1.55 billion cu m (2009 est.)
Natural gas - consumption World Ranking: 69
3.25 billion cu m (2009 est.)
Natural gas - exports World Ranking: 119
0 cu m (2009 est.)
Natural gas - imports World Ranking: 50
1.7 billion cu m (2009 est.)
Natural gas - proved reserves World Ranking: 46
198.2 billion cu m (1 January 2011 est.) Current account balance World Ranking: 51
$191 million (2011 est.)
$6.335 billion (2010 est.) Exports World Ranking: 53
$62.85 billion (2011 est.)
$56.09 billion (2010 est.) Exports - commodities
Machinery and equipment, software, cut diamonds, agricultural products, chemicals, textiles and apparel Exports - partners
US 28.8%, Hong Kong 7.9%, Belgium 5.6%, UK 5%, India 4.5%, China 4% (2011) Imports World Ranking: 44
$71.93 billion (2011 est.)
$58.04 billion (2010 est.) Imports - commodities
Raw materials, military equipment, investment goods, rough diamonds, fuels, grain, consumer goods Imports - partners
US 11.8%, China 7.4%, Germany 6.2%, Belgium 6.1%, Switzerland 5.4%, Italy 4.2% (2011) Reserves of foreign exchange and gold World Ranking: 29
$74.87 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $70.91 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Debt - external World Ranking: 44
$102.3 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $106.4 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Stock of direct foreign investment - at home World Ranking: 49
$66.57 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $60.19 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad World Ranking: 30
$69.83 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $66.3 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Exchange rates
New Israeli shekels (ILS) per US dollar - 3.5781 (2011 est.)3.739 (2010 est.) 3.93 (2009) 3.588 (2008) 4.14 (2007) Fiscal year
Calendar year
Comments
Add a new comment: |
Advertisement
Members area
Israel (Jerusalem):
GPS points from Israel (Jerusalem)
|
||||||||
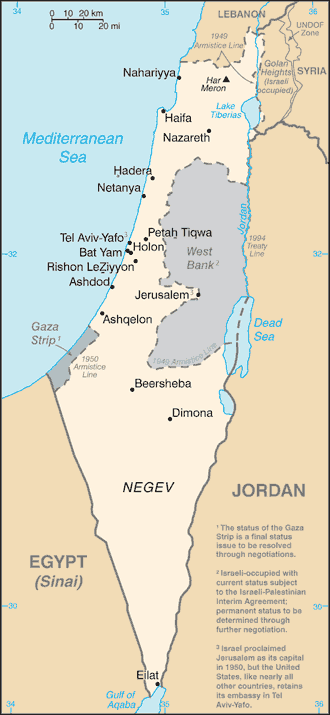
 Following World War II, the British withdrew from their mandate of Palestine, and the UN partitioned the area into Arab and Jewish states, an arrangement rejected by the Arabs. Subsequently, the Israelis defeated the Arabs in a series of wars without ending the deep tensions between the two sides. The territories Israel occupied since the 1967 war are not included in the Israel country profile, unless otherwise noted. On 25 April 1982, Israel withdrew from the Sinai pursuant to the 1979 Israel-Egypt Peace Treaty. In keeping with the framework established at the Madrid Conference in October 1991, bilateral negotiations were conducted between Israel and Palestinian representatives and Syria to achieve a permanent settlement. Israel and Palestinian officials signed on 13 September 1993 a Declaration of Principles (also known as the "Oslo Accords") guiding an interim period of Palestinian self-rule. Outstanding territorial and other disputes with Jordan were resolved in the 26 October 1994 Israel-Jordan Treaty of Peace. In addition, on 25 May 2000, Israel withdrew unilaterally from southern Lebanon, which it had occupied since 1982. In April 2003, US President BUSH, working in conjunction with the EU, UN, and Russia - the "Quartet" - took the lead in laying out a roadmap to a final settlement of the conflict by 2005, based on reciprocal steps by the two parties leading to two states, Israel and a democratic Palestine. However, progress toward a permanent status agreement was undermined by Israeli-Palestinian violence between September 2003 and February 2005. In the summer of 2005, Israel unilaterally disengaged from the Gaza Strip, evacuating settlers and its military while retaining control over most points of entry into the Gaza Strip. The election of HAMAS to head the Palestinian Legislative Council froze relations between Israel and the Palestinian Authority (PA). Ehud OLMERT became prime minister in March 2006 and presided over a 34-day conflict with Hizballah in Lebanon in June-August 2006 and a 23-day conflict with HAMAS in the Gaza Strip during December 2008 and January 2009. OLMERT, who in June 2007 resumed talks with PA President Mahmoud ABBAS, resigned in September 2008. Prime Minister Binyamin NETANYAHU formed a coalition in March 2009 following a February 2009 general election. Direct talks launched in September 2010 collapsed following the expiration of Israel's 10-month partial settlement construction moratorium in the West Bank.
Following World War II, the British withdrew from their mandate of Palestine, and the UN partitioned the area into Arab and Jewish states, an arrangement rejected by the Arabs. Subsequently, the Israelis defeated the Arabs in a series of wars without ending the deep tensions between the two sides. The territories Israel occupied since the 1967 war are not included in the Israel country profile, unless otherwise noted. On 25 April 1982, Israel withdrew from the Sinai pursuant to the 1979 Israel-Egypt Peace Treaty. In keeping with the framework established at the Madrid Conference in October 1991, bilateral negotiations were conducted between Israel and Palestinian representatives and Syria to achieve a permanent settlement. Israel and Palestinian officials signed on 13 September 1993 a Declaration of Principles (also known as the "Oslo Accords") guiding an interim period of Palestinian self-rule. Outstanding territorial and other disputes with Jordan were resolved in the 26 October 1994 Israel-Jordan Treaty of Peace. In addition, on 25 May 2000, Israel withdrew unilaterally from southern Lebanon, which it had occupied since 1982. In April 2003, US President BUSH, working in conjunction with the EU, UN, and Russia - the "Quartet" - took the lead in laying out a roadmap to a final settlement of the conflict by 2005, based on reciprocal steps by the two parties leading to two states, Israel and a democratic Palestine. However, progress toward a permanent status agreement was undermined by Israeli-Palestinian violence between September 2003 and February 2005. In the summer of 2005, Israel unilaterally disengaged from the Gaza Strip, evacuating settlers and its military while retaining control over most points of entry into the Gaza Strip. The election of HAMAS to head the Palestinian Legislative Council froze relations between Israel and the Palestinian Authority (PA). Ehud OLMERT became prime minister in March 2006 and presided over a 34-day conflict with Hizballah in Lebanon in June-August 2006 and a 23-day conflict with HAMAS in the Gaza Strip during December 2008 and January 2009. OLMERT, who in June 2007 resumed talks with PA President Mahmoud ABBAS, resigned in September 2008. Prime Minister Binyamin NETANYAHU formed a coalition in March 2009 following a February 2009 general election. Direct talks launched in September 2010 collapsed following the expiration of Israel's 10-month partial settlement construction moratorium in the West Bank.