
|
|
Advertisements:
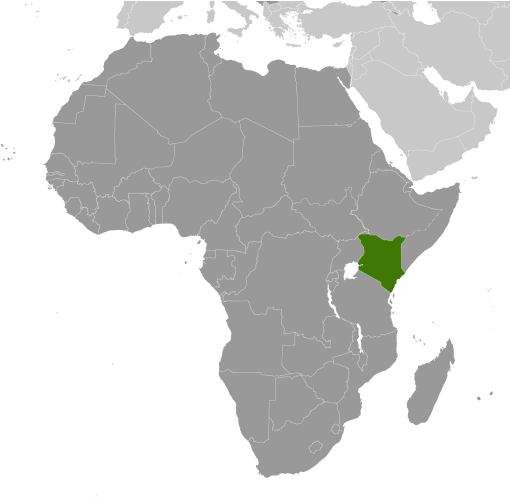
GeographyLocation
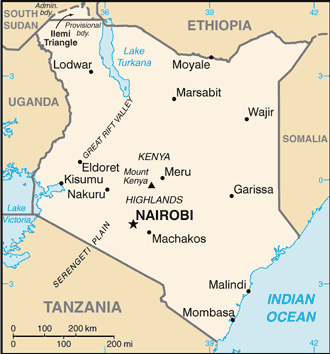
Eastern Africa, bordering the Indian Ocean, between Somalia and Tanzania Geographic coordinates
1 00 N, 38 00 E
Map references
Africa
Area World Ranking: 49
Total 580,367 sq km
Land 569,140 sq km Water 11,227 sq km Area - comparative
Slightly more than twice the size of Nevada Land boundaries
Total 3,477 km
Border countries Ethiopia 861 km, Somalia 682 km, South Sudan 232 km, Tanzania 769 km, Uganda 933 km Coastline
536 km
Maritime claims
Territorial sea 12 nm
Exclusive economic zone 200 nm Continental shelf 200 m depth or to the depth of exploitation Climate
Varies from tropical along coast to arid in interior Terrain
Low plains rise to central highlands bisected by Great Rift Valley; fertile plateau in west Elevation extremes
Lowest point Indian Ocean 0 m
Highest point Mount Kenya 5,199 m Natural resources
Limestone, soda ash, salt, gemstones, fluorspar, zinc, diatomite, gypsum, wildlife, hydropower Land use
Arable land 8.01%
Permanent crops 0.97% Other 91.02% (2005) Irrigated land
1,030 sq km (2003)
Total renewable water resources
30.2 cu km (1990)
Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural)
Total 1.58 cu km/yr (30%/6%/64%)
Per capita 46 cu m/yr (2000) Natural hazards
Recurring drought; flooding during rainy seasons Volcanism Limited volcanic activity; the Barrier (elev. 1,032 m) last erupted in 1921; South Island is the only other historically active volcano Environment - current issues
Water pollution from urban and industrial wastes; degradation of water quality from increased use of pesticides and fertilizers; water hyacinth infestation in Lake Victoria; deforestation; soil erosion; desertification; poaching Environment - international agreements
Party to
Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling Signed, but not ratified None of the selected agreements Geography - note
The Kenyan Highlands comprise one of the most successful agricultural production regions in Africa; glaciers are found on Mount Kenya, Africa's second highest peak; unique physiography supports abundant and varied wildlife of scientific and economic value
Comments
Add a new comment: |
Advertisement
Members area
Kenya (Nairobi):
GPS points from Kenya (Nairobi)
|
||||||||
 Founding president and liberation struggle icon Jomo KENYATTA led Kenya from independence in 1963 until his death in 1978, when President Daniel Toroitich arap MOI took power in a constitutional succession. The country was a de facto one-party state from 1969 until 1982 when the ruling Kenya African National Union (KANU) made itself the sole legal party in Kenya. MOI acceded to internal and external pressure for political liberalization in late 1991. The ethnically fractured opposition failed to dislodge KANU from power in elections in 1992 and 1997, which were marred by violence and fraud, but were viewed as having generally reflected the will of the Kenyan people. President MOI stepped down in December 2002 following fair and peaceful elections. Mwai KIBAKI, running as the candidate of the multiethnic, united opposition group, the National Rainbow Coalition (NARC), defeated KANU candidate Uhuru KENYATTA and assumed the presidency following a campaign centered on an anticorruption platform. KIBAKI's NARC coalition splintered in 2005 over a constitutional review process. Government defectors joined with KANU to form a new opposition coalition, the Orange Democratic Movement (ODM), which defeated the government's draft constitution in a popular referendum in November 2005. KIBAKI's reelection in December 2007 brought charges of vote rigging from ODM candidate Raila ODINGA and unleashed two months of violence in which as many as 1,500 people died. UN-sponsored talks in late February 2008 produced a power-sharing accord bringing ODINGA into the government in the restored position of prime minister. Kenya in August 2010 adopted a new constitution that eliminates the role of prime minister after the next presidential election.
Founding president and liberation struggle icon Jomo KENYATTA led Kenya from independence in 1963 until his death in 1978, when President Daniel Toroitich arap MOI took power in a constitutional succession. The country was a de facto one-party state from 1969 until 1982 when the ruling Kenya African National Union (KANU) made itself the sole legal party in Kenya. MOI acceded to internal and external pressure for political liberalization in late 1991. The ethnically fractured opposition failed to dislodge KANU from power in elections in 1992 and 1997, which were marred by violence and fraud, but were viewed as having generally reflected the will of the Kenyan people. President MOI stepped down in December 2002 following fair and peaceful elections. Mwai KIBAKI, running as the candidate of the multiethnic, united opposition group, the National Rainbow Coalition (NARC), defeated KANU candidate Uhuru KENYATTA and assumed the presidency following a campaign centered on an anticorruption platform. KIBAKI's NARC coalition splintered in 2005 over a constitutional review process. Government defectors joined with KANU to form a new opposition coalition, the Orange Democratic Movement (ODM), which defeated the government's draft constitution in a popular referendum in November 2005. KIBAKI's reelection in December 2007 brought charges of vote rigging from ODM candidate Raila ODINGA and unleashed two months of violence in which as many as 1,500 people died. UN-sponsored talks in late February 2008 produced a power-sharing accord bringing ODINGA into the government in the restored position of prime minister. Kenya in August 2010 adopted a new constitution that eliminates the role of prime minister after the next presidential election.