
|
|
Advertisements:
EconomyEconomy - overview
Russia has undergone significant changes since the collapse of the Soviet Union, moving from a globally-isolated, centrally-planned economy to a more market-based and globally-integrated economy. Economic reforms in the 1990s privatized most industry, with notable exceptions in the energy and defense-related sectors. The protection of property rights is still weak and the private sector remains subject to heavy state interference. Russian industry is primarily split between globally-competitive commodity producers. In 2011, Russia became the world's leading oil producer, surpassing Saudi Arabia; Russia is the second-largest producer of natural gas; Russia holds the world's largest natural gas reserves, the second-largest coal reserves, and the eighth-largest crude oil reserves. Russia is the third-largest exporter of both steel and primary aluminum. Other less competitive heavy industries remain dependent on the Russian domestic market. Russia's reliance on commodity exports makes it vulnerable to boom and bust cycles that follow the highly volatile swings in global commodity prices. The government since 2007 has embarked on an ambitious program to reduce this dependency and build up the country's high technology sectors, but with few results so far. The economy had averaged 7% growth in the decade following the 1998 Russian financial crisis, resulting in a doubling of real disposable incomes and the emergence of a middle class. The Russian economy, however, was one of the hardest hit by the 2008-09 global economic crisis as oil prices plummeted and the foreign credits that Russian banks and firms relied on dried up. According to the World Bank the government's anti-crisis package in 2008-09 amounted to roughly 6.7% of GDP. The Central Bank of Russia spent one-third of its $600 billion international reserves, the world's third largest, in late 2008 to slow the devaluation of the ruble. The government also devoted $200 billion in a rescue plan to increase liquidity in the banking sector and aid Russian firms unable to roll over large foreign debts coming due. The economic decline bottomed out in mid-2009 and the economy began to grow in the third quarter of 2009. However, a severe drought and fires in central Russia reduced agricultural output, prompting a ban on grain exports for part of the year, and slowed growth in other sectors such as manufacturing and retail trade. High oil prices buoyed Russian growth in 2011 and helped Russia reduce the budget deficit inherited from the lean years of 2008-09. Russia has reduced unemployment since 2009 and has made progress on reducing inflation since 2010. Russia's long-term challenges include a shrinking workforce, a high level of corruption, difficulty in accessing capital for smaller, non-energy companies, and poor infrastructure in need of large investments. Gdp (purchasing power parity) World Ranking: 7
$2.414 trillion (2011 est.)
$2.314 trillion (2010 est.) $2.219 trillion (2009 est.) Note Data are in 2011 US dollars Gdp (official exchange rate)
$1.85 trillion (2011 est.)
Gdp - real growth rate World Ranking: 87
4.3% (2011 est.)
4.3% (2010 est.) -7.8% (2009 est.) Gdp - per capita (ppp) World Ranking: 71
$17,000 (2011 est.)
$16,200 (2010 est.) $15,600 (2009 est.) Note Data are in 2011 US dollars Gdp - composition by sector
Agriculture 4.5%
Industry 36.9% Services 58.6% (2011 est.) Labor force World Ranking: 8
75.41 million (2011 est.)
Labor force - by occupation
Agriculture 9.8%
Industry 27.5% Services 62.7% (2010) Unemployment rate World Ranking: 74
6.6% (2011 est.)
7.5% (2010 est.) Population below poverty line
13.1% (2010)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
Lowest 10% 2.8%
Highest 10% 31.7% (2009 est.) Distribution of family income - gini index World Ranking: 52
42 (2010)
39.9 (2001) Investment (gross fixed) World Ranking: 75
21.3% of GDP (2011 est.)
Budget
Revenues $382.8 billion
Expenditures $376.2 billion (2011 est.) Taxes and other revenues World Ranking: 157
20.7% of GDP (2011 est.)
Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-) World Ranking: 41
0.4% of GDP (2011 est.)
Public debt World Ranking: 134
8.3% of GDP (2011 est.)
9.4% of GDP (2010 est.) Note Data cover general government debt, and includes debt instruments issued (or owned) by government entities other than the treasury; the data include treasury debt held by foreign entities; the data include debt issued by subnational entities, as well as intra-governmental debt; intra-governmental debt consists of treasury borrowings from surpluses in the social funds, such as for retirement, medical care, and unemployment. Debt instruments for the social funds are not sold at public auctions. Inflation rate (consumer prices) World Ranking: 176
8.4% (2011 est.)
6.9% (2010 est.) Central bank discount rate World Ranking: 34
5.5% (31 December 2010 est.)
8.75% (31 December 2009 est.) Commercial bank prime lending rate World Ranking: 80
8.46% (31 December 2011 est.)
10.817% (31 December 2010 est.) Stock of narrow money World Ranking: 12
$398.2 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $268.7 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Stock of broad money World Ranking: 20
$895 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $780.6 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Stock of domestic credit World Ranking: 20
$759.6 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $573.2 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Market value of publicly traded shares World Ranking: 17
$796.4 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $1.005 trillion (31 December 2010) $861.4 billion (31 December 2009 est.) Agriculture - products
Grain, sugar beets, sunflower seed, vegetables, fruits; beef, milk Industries
Complete range of mining and extractive industries producing coal, oil, gas, chemicals, and metals; all forms of machine building from rolling mills to high-performance aircraft and space vehicles; defense industries including radar, missile production, and advanced electronic components, shipbuilding; road and rail transportation equipment; communications equipment; agricultural machinery, tractors, and construction equipment; electric power generating and transmitting equipment; medical and scientific instruments; consumer durables, textiles, foodstuffs, handicrafts Industrial production growth rate World Ranking: 73
4.7% (2011 est.)
Electricity - production World Ranking: 4
925.9 billion kWh (2009 est.)
Electricity - consumption World Ranking: 5
857.6 billion kWh (2008 est.)
Electricity - exports
17.7 billion kWh (2009 est.)
Electricity - imports
14.63 billion kWh (2009 est.)
Oil - production World Ranking: 2
10.27 million bbl/day (2010)
Oil - consumption World Ranking: 9
2.199 million bbl/day (2010)
Oil - exports World Ranking: 2
5.01 million bbl/day (2010 est.) Oil - imports World Ranking: 91
42,750 bbl/day (2009 est.)
Oil - proved reserves World Ranking: 8
60 billion bbl (1 January 2011 est.) Natural gas - production World Ranking: 2
588.9 billion cu m (2010)
Natural gas - consumption World Ranking: 3
414.1 billion cu m (2010)
Natural gas - exports World Ranking: 1
199.9 billion cu m (2010 est.)
Natural gas - imports World Ranking: 9
38.2 billion cu m (2010 est.)
Natural gas - proved reserves World Ranking: 1
44.8 trillion cu m (1 January 2011 est.) Current account balance World Ranking: 5
$101.3 billion (2011 est.)
$71.13 billion (2010 est.) Exports World Ranking: 10
$520.9 billion (2011 est.)
$400.1 billion (2010 est.) Exports - commodities
Petroleum and petroleum products, natural gas, metals, wood and wood products, chemicals, and a wide variety of civilian and military manufactures Exports - partners
Netherlands 12.3%, China 6.5%, Italy 5.6%, Germany 4.6%, Poland 4.3% (2011) Imports World Ranking: 18
$322.5 billion (2011 est.)
$248.7 billion (2010 est.) Imports - commodities
Machinery, vehicles, pharmaceutical products, plastic, semi-finished metal products, meat, fruits and nuts, optical and medical instruments, iron, steel Imports - partners
China 15.6%, Germany 10%, Ukraine 6.6%, Italy 4.3% (2011) Reserves of foreign exchange and gold World Ranking: 5
$498.6 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $479.4 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Debt - external World Ranking: 25
$519.4 billion (30 September 2011 est.) $538.6 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Stock of direct foreign investment - at home World Ranking: 13
$542.9 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $493.4 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad World Ranking: 14
$409.1 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $369.1 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Exchange rates
Russian rubles (RUB) per US dollar - 29.382 (2011 est.)30.368 (2010 est.) 31.74 (2009) 24.853 (2008) 25.581 (2007) Fiscal year
Calendar year
Comments
Add a new comment: |
Advertisement
Members area
Russia (Moscow):
GPS points from Russia (Moscow)
|
||||||||
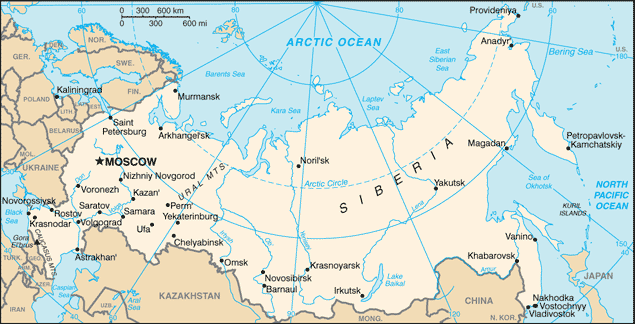
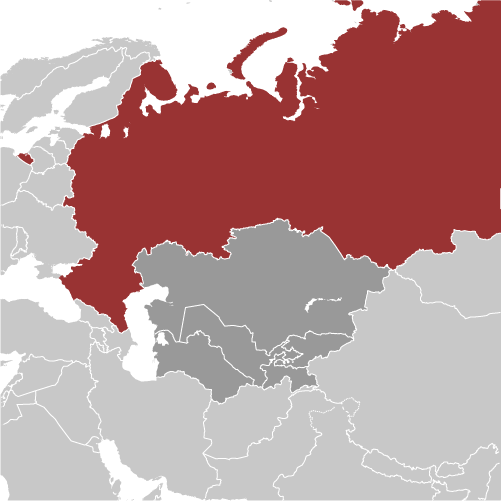
 Founded in the 12th century, the Principality of Muscovy, was able to emerge from over 200 years of Mongol domination (13th-15th centuries) and to gradually conquer and absorb surrounding principalities. In the early 17th century, a new Romanov Dynasty continued this policy of expansion across Siberia to the Pacific. Under PETER I (ruled 1682-1725), hegemony was extended to the Baltic Sea and the country was renamed the Russian Empire. During the 19th century, more territorial acquisitions were made in Europe and Asia. Defeat in the Russo-Japanese War of 1904-05 contributed to the Revolution of 1905, which resulted in the formation of a parliament and other reforms. Repeated devastating defeats of the Russian army in World War I led to widespread rioting in the major cities of the Russian Empire and to the overthrow in 1917 of the imperial household. The Communists under Vladimir LENIN seized power soon after and formed the USSR. The brutal rule of Iosif STALIN (1928-53) strengthened Communist rule and Russian dominance of the Soviet Union at a cost of tens of millions of lives. The Soviet economy and society stagnated in the following decades until General Secretary Mikhail GORBACHEV (1985-91) introduced glasnost (openness) and perestroika (restructuring) in an attempt to modernize Communism, but his initiatives inadvertently released forces that by December 1991 splintered the USSR into Russia and 14 other independent republics. Since then, Russia has shifted its post-Soviet democratic ambitions in favor of a centralized semi-authoritarian state in which the leadership seeks to legitimize its rule through managed national elections, populist appeals by former President PUTIN, and continued economic growth. Russia has severely disabled a Chechen rebel movement, although violence still occurs throughout the North Caucasus.
Founded in the 12th century, the Principality of Muscovy, was able to emerge from over 200 years of Mongol domination (13th-15th centuries) and to gradually conquer and absorb surrounding principalities. In the early 17th century, a new Romanov Dynasty continued this policy of expansion across Siberia to the Pacific. Under PETER I (ruled 1682-1725), hegemony was extended to the Baltic Sea and the country was renamed the Russian Empire. During the 19th century, more territorial acquisitions were made in Europe and Asia. Defeat in the Russo-Japanese War of 1904-05 contributed to the Revolution of 1905, which resulted in the formation of a parliament and other reforms. Repeated devastating defeats of the Russian army in World War I led to widespread rioting in the major cities of the Russian Empire and to the overthrow in 1917 of the imperial household. The Communists under Vladimir LENIN seized power soon after and formed the USSR. The brutal rule of Iosif STALIN (1928-53) strengthened Communist rule and Russian dominance of the Soviet Union at a cost of tens of millions of lives. The Soviet economy and society stagnated in the following decades until General Secretary Mikhail GORBACHEV (1985-91) introduced glasnost (openness) and perestroika (restructuring) in an attempt to modernize Communism, but his initiatives inadvertently released forces that by December 1991 splintered the USSR into Russia and 14 other independent republics. Since then, Russia has shifted its post-Soviet democratic ambitions in favor of a centralized semi-authoritarian state in which the leadership seeks to legitimize its rule through managed national elections, populist appeals by former President PUTIN, and continued economic growth. Russia has severely disabled a Chechen rebel movement, although violence still occurs throughout the North Caucasus.