
|
|
Advertisements:
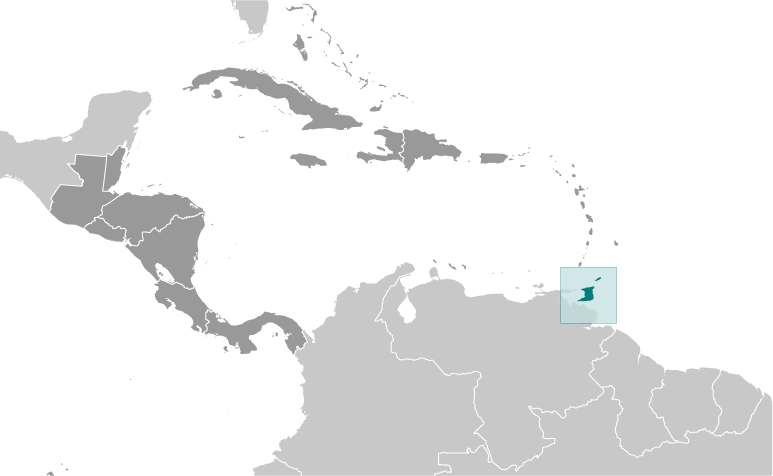
GeographyLocation
Caribbean, islands between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, northeast of Venezuela Geographic coordinates
11 00 N, 61 00 W
Map references
Central America and the Caribbean
Area World Ranking: 174
Total 5,128 sq km
Land 5,128 sq km Water 0 sq km Area - comparative
Slightly smaller than Delaware
Land boundaries
0 km
Coastline
362 km
Maritime claims
Measured from claimed archipelagic baselines Territorial sea 12 nmContiguous zone 24 nm Exclusive economic zone 200 nm Continental shelf 200 nm or to the outer edge of the continental margin Climate
Tropical; rainy season (June to December) Terrain
Mostly plains with some hills and low mountains Elevation extremes
Lowest point Caribbean Sea 0 m
Highest point El Cerro del Aripo 940 m Natural resources
Petroleum, natural gas, asphalt Land use
Arable land 14.62%
Permanent crops 9.16% Other 76.22% (2005) Irrigated land
70 sq km (2003)
Total renewable water resources
3.8 cu km (2000)
Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural)
Total 0.31 cu km/yr (68%/26%/6%)
Per capita 237 cu m/yr (2000) Natural hazards
Outside usual path of hurricanes and other tropical storms Environment - current issues
Water pollution from agricultural chemicals, industrial wastes, and raw sewage; oil pollution of beaches; deforestation; soil erosion Environment - international agreements
Party to
Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands Signed, but not ratified None of the selected agreements Geography - note
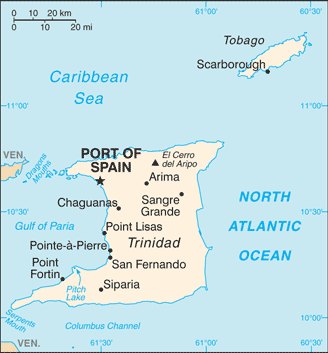
Pitch Lake, on Trinidad's southwestern coast, is the world's largest natural reservoir of asphalt
Comments
Add a new comment: |
Advertisement
Members area
Trinidad And Tobago (Port-of-spain):
GPS points from Trinidad And Tobago (Port-of-spain)
|
||||||||
 First colonized by the Spanish, the islands came under British control in the early 19th century. The islands' sugar industry was hurt by the emancipation of the slaves in 1834. Manpower was replaced with the importation of contract laborers from India between 1845 and 1917, which boosted sugar production as well as the cocoa industry. The discovery of oil on Trinidad in 1910 added another important export. Independence was attained in 1962. The country is one of the most prosperous in the Caribbean thanks largely to petroleum and natural gas production and processing. Tourism, mostly in Tobago, is targeted for expansion and is growing. The government is coping with a rise in violent crime.
First colonized by the Spanish, the islands came under British control in the early 19th century. The islands' sugar industry was hurt by the emancipation of the slaves in 1834. Manpower was replaced with the importation of contract laborers from India between 1845 and 1917, which boosted sugar production as well as the cocoa industry. The discovery of oil on Trinidad in 1910 added another important export. Independence was attained in 1962. The country is one of the most prosperous in the Caribbean thanks largely to petroleum and natural gas production and processing. Tourism, mostly in Tobago, is targeted for expansion and is growing. The government is coping with a rise in violent crime.