
|
|
Advertisements:
EconomyEconomy - overview
After Russia, the Ukrainian republic was the most important economic component of the former Soviet Union, producing about four times the output of the next-ranking republic. Its fertile black soil generated more than one-fourth of Soviet agricultural output, and its farms provided substantial quantities of meat, milk, grain, and vegetables to other republics. Likewise, its diversified heavy industry supplied the unique equipment (for example, large diameter pipes) and raw materials to industrial and mining sites (vertical drilling apparatus) in other regions of the former USSR. Shortly after independence in August 1991, the Ukrainian Government liberalized most prices and erected a legal framework for privatization, but widespread resistance to reform within the government and the legislature soon stalled reform efforts and led to some backtracking. Output by 1999 had fallen to less than 40% of the 1991 level. Ukraine's dependence on Russia for energy supplies and the lack of significant structural reform have made the Ukrainian economy vulnerable to external shocks. Ukraine depends on imports to meet about three-fourths of its annual oil and natural gas requirements and 100% of its nuclear fuel needs. After a two-week dispute that saw gas supplies cutoff to Europe, Ukraine agreed to 10-year gas supply and transit contracts with Russia in January 2009 that brought gas prices to "world" levels. The strict terms of the contracts have further hobbled Ukraine's cash-strapped state gas company, Naftohaz. Outside institutions - particularly the IMF - have encouraged Ukraine to quicken the pace and scope of reforms. Ukrainian Government officials eliminated most tax and customs privileges in a March 2005 budget law, bringing more economic activity out of Ukraine's large shadow economy, but more improvements are needed, including fighting corruption, developing capital markets, and improving the legislative framework. Ukraine's economy was buoyant despite political turmoil between the prime minister and president until mid-2008. Real GDP growth exceeded 7% in 2006-07, fueled by high global prices for steel - Ukraine's top export - and by strong domestic consumption, spurred by rising pensions and wages. A drop in steel prices and Ukraine's exposure to the global financial crisis due to aggressive foreign borrowing lowered growth in 2008. Ukraine reached an agreement with the IMF for a $16.4 billion Stand-By Arrangement in November 2008 to deal with the economic crisis, but the program quickly stalled due to the Ukrainian Government's lack of progress in implementing reforms. The economy contracted nearly 15% in 2009, among the worst economic performances in the world. In April 2010, Ukraine negotiated a price discount on Russian gas imports in exchange for extending Russia's lease on its naval base in Crimea. In August 2010, Ukraine, under the YANUKOVYCH Administration, reached a new agreement with the IMF for a $15.1 billion Stand-By Agreement to put the country on the path to fiscal sustainability, reform the gas sector, and shore up the country's banking system. Economic growth resumed in 2010 and 2011, buoyed by exports. After initial disbursements, the IMF program stalled in early 2011 due to the Ukrainian Government's lack of progress in implementing key gas sector reforms, namely gas tariff increases. Gdp (purchasing power parity) World Ranking: 39
$333.7 billion (2011 est.)
$317.2 billion (2010 est.) $304.7 billion (2009 est.) Note Data are in 2011 US dollars Gdp (official exchange rate)
$165 billion (2011 est.)
Gdp - real growth rate World Ranking: 64
5.2% (2011 est.)
4.1% (2010 est.) -14.8% (2009 est.) Gdp - per capita (ppp) World Ranking: 134
$7,300 (2011 est.)
$6,900 (2010 est.) $6,600 (2009 est.) Note Data are in 2011 US dollars Gdp - composition by sector
Agriculture 9.4%
Industry 34.4% Services 56.2% (2011 est.) Labor force World Ranking: 30
22.09 million (2011 est.)
Labor force - by occupation
Agriculture 15.8%
Industry 18.5% Services 65.7% (2008) Unemployment rate World Ranking: 81
7% (2011 est.)
8.1% (2010 est.) Note Officially registered; large number of unregistered or underemployed workers Population below poverty line
35% (2009)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
Lowest 10% 4.2%
Highest 10% 22% (2009 est.) Distribution of family income - gini index World Ranking: 122
27.5 (2008)
29 (1999) Investment (gross fixed) World Ranking: 96
20% of GDP (2011 est.)
Budget
Revenues $49.99 billion
Expenditures $56.39 billion Note This is the planned, consolidated budget (2011 est.) Taxes and other revenues World Ranking: 89
30.3% of GDP (2011 est.)
Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-) World Ranking: 121
-3.9% of GDP (2011 est.)
Public debt World Ranking: 83
39% of GDP (2011 est.)
39.5% of GDP (2010 est.) Inflation rate (consumer prices) World Ranking: 168
8% (2011 est.)
9.4% (2010 est.) Central bank discount rate World Ranking: 27
11.97% (31 December 2010 est.)
10.25% (31 December 2009 est.) Commercial bank prime lending rate World Ranking: 36
15.95% (31 December 2011 est.)
15.869% (31 December 2010 est.) Stock of narrow money World Ranking: 48
$45.43 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $36.41 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Stock of broad money World Ranking: 56
$85.8 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $74.96 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Stock of domestic credit World Ranking: 49
$121 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $108.1 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Market value of publicly traded shares World Ranking: 53
$25.56 billion (31 December 2011) $39.46 billion (31 December 2010) $16.79 billion (31 December 2009) Agriculture - products
Grain, sugar beets, sunflower seeds, vegetables; beef, milk Industries
Coal, electric power, ferrous and nonferrous metals, machinery and transport equipment, chemicals, food processing Industrial production growth rate World Ranking: 32
7.6% (2011 est.)
Electricity - production World Ranking: 21
172.9 billion kWh (2009 est.)
Electricity - consumption World Ranking: 22
134.6 billion kWh (2009 est.)
Electricity - exports
4 billion kWh (2009 est.)
Electricity - imports
6.73 billion kWh (2008 est.)
Oil - production World Ranking: 55
82,000 bbl/day (2010 est.)
Oil - consumption World Ranking: 43
296,000 bbl/day (2010 est.)
Oil - exports World Ranking: 61
114,000 bbl/day (2009 est.)
Oil - imports World Ranking: 34
301,900 bbl/day (2009 est.)
Oil - proved reserves World Ranking: 54
395 million bbl (1 January 2011 est.) Natural gas - production World Ranking: 31
20.26 billion cu m (2009 est.)
Natural gas - consumption World Ranking: 19
44.16 billion cu m (2009 est.)
Natural gas - exports World Ranking: 35
2.8 billion cu m (2009 est.)
Natural gas - imports World Ranking: 13
26.7 billion cu m (2009 est.)
Natural gas - proved reserves World Ranking: 24
1.104 trillion cu m (1 January 2011 est.) Current account balance World Ranking: 175
-$9.006 billion (2011 est.)
-$3.018 billion (2010 est.) Exports World Ranking: 51
$69.42 billion (2011 est.)
$52.19 billion (2010 est.) Exports - commodities
Ferrous and nonferrous metals, fuel and petroleum products, chemicals, machinery and transport equipment, food products Exports - partners
Russia 27.3%, Turkey 5.9%, Italy 4.7% (2009 est.) Imports World Ranking: 38
$83.22 billion (2011 est.)
$60.58 billion (2010 est.) Imports - commodities
Energy, machinery and equipment, chemicals Imports - partners
Russia 30.8%, Germany 9.1%, China 8.9%, Poland 5.3%, Belarus 5% (2009 est.) Reserves of foreign exchange and gold World Ranking: 47
$31.79 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $34.58 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Debt - external World Ranking: 40
$123.7 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $116.8 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Stock of direct foreign investment - at home World Ranking: 52
$60.51 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $53.3 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad World Ranking: 65
$2.995 billion (31 December 2011 est.) $2.803 billion (31 December 2010 est.) Exchange rates
Hryvnia (UAH) per US dollar -
7.9676 (2011 est.) 7.9356 (2010 est.) 7.7912 (2009) 4.9523 (2008) 5.05 (2007) Fiscal year
Calendar year
Comments
Add a new comment: |
Advertisement
Members area
Ukraine (Kiev):
GPS points from Ukraine (Kiev)
|
||||||||
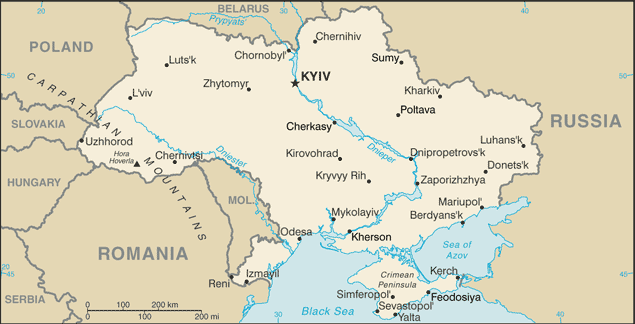
 Ukraine was the center of the first eastern Slavic state, Kyivan Rus, which during the 10th and 11th centuries was the largest and most powerful state in Europe. Weakened by internecine quarrels and Mongol invasions, Kyivan Rus was incorporated into the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and eventually into the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. The cultural and religious legacy of Kyivan Rus laid the foundation for Ukrainian nationalism through subsequent centuries. A new Ukrainian state, the Cossack Hetmanate, was established during the mid-17th century after an uprising against the Poles. Despite continuous Muscovite pressure, the Hetmanate managed to remain autonomous for well over 100 years. During the latter part of the 18th century, most Ukrainian ethnographic territory was absorbed by the Russian Empire. Following the collapse of czarist Russia in 1917, Ukraine was able to achieve a short-lived period of independence (1917-20), but was reconquered and forced to endure a brutal Soviet rule that engineered two forced famines (1921-22 and 1932-33) in which over 8 million died. In World War II, German and Soviet armies were responsible for some 7 to 8 million more deaths. Although final independence for Ukraine was achieved in 1991 with the dissolution of the USSR, democracy and prosperity remained elusive as the legacy of state control and endemic corruption stalled efforts at economic reform, privatization, and civil liberties. A peaceful mass protest "Orange Revolution" in the closing months of 2004 forced the authorities to overturn a rigged presidential election and to allow a new internationally monitored vote that swept into power a reformist slate under Viktor YUSHCHENKO. Subsequent internal squabbles in the YUSHCHENKO camp allowed his rival Viktor YANUKOVYCH to stage a comeback in parliamentary elections and become prime minister in August of 2006. An early legislative election, brought on by a political crisis in the spring of 2007, saw Yuliya TYMOSHENKO, as head of an "Orange" coalition, installed as a new prime minister in December 2007. Viktor YANUKOVUYCH was elected president in a February 2010 run-off election that observers assessed as meeting most international standards. The following month, the Rada approved a vote of no-confidence prompting Yuliya TYMOSHENKO to resign from her post as prime minister.
Ukraine was the center of the first eastern Slavic state, Kyivan Rus, which during the 10th and 11th centuries was the largest and most powerful state in Europe. Weakened by internecine quarrels and Mongol invasions, Kyivan Rus was incorporated into the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and eventually into the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. The cultural and religious legacy of Kyivan Rus laid the foundation for Ukrainian nationalism through subsequent centuries. A new Ukrainian state, the Cossack Hetmanate, was established during the mid-17th century after an uprising against the Poles. Despite continuous Muscovite pressure, the Hetmanate managed to remain autonomous for well over 100 years. During the latter part of the 18th century, most Ukrainian ethnographic territory was absorbed by the Russian Empire. Following the collapse of czarist Russia in 1917, Ukraine was able to achieve a short-lived period of independence (1917-20), but was reconquered and forced to endure a brutal Soviet rule that engineered two forced famines (1921-22 and 1932-33) in which over 8 million died. In World War II, German and Soviet armies were responsible for some 7 to 8 million more deaths. Although final independence for Ukraine was achieved in 1991 with the dissolution of the USSR, democracy and prosperity remained elusive as the legacy of state control and endemic corruption stalled efforts at economic reform, privatization, and civil liberties. A peaceful mass protest "Orange Revolution" in the closing months of 2004 forced the authorities to overturn a rigged presidential election and to allow a new internationally monitored vote that swept into power a reformist slate under Viktor YUSHCHENKO. Subsequent internal squabbles in the YUSHCHENKO camp allowed his rival Viktor YANUKOVYCH to stage a comeback in parliamentary elections and become prime minister in August of 2006. An early legislative election, brought on by a political crisis in the spring of 2007, saw Yuliya TYMOSHENKO, as head of an "Orange" coalition, installed as a new prime minister in December 2007. Viktor YANUKOVUYCH was elected president in a February 2010 run-off election that observers assessed as meeting most international standards. The following month, the Rada approved a vote of no-confidence prompting Yuliya TYMOSHENKO to resign from her post as prime minister.