|

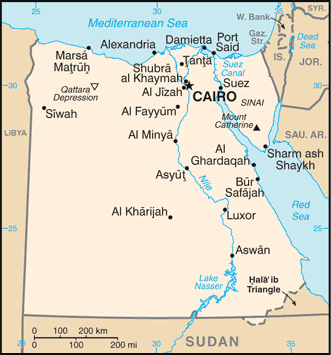
Administrative divisions (GPS Maps)
Geography
People and Society
Government
Economy
Communications
Transportation
Military |
 |
 The regularity and richness of the annual Nile River flood, coupled with semi-isolation provided by deserts to the east and west, allowed for the development of one of the world's great civilizations. A unified kingdom arose circa 3200 B.C., and a series of dynasties ruled in Egypt for the next three millennia. The last native dynasty fell to the Persians in 341 B.C., who in turn were replaced by the Greeks, Romans, and Byzantines. It was the Arabs who introduced Islam and the Arabic language in the 7th century and who ruled for the next six centuries. A local military caste, the Mamluks took control about 1250 and continued to govern after the conquest of Egypt by the Ottoman Turks in 1517. Following the completion of the Suez Canal in 1869, Egypt became an important world transportation hub, but also fell heavily into debt. Ostensibly to protect its investments, Britain seized control of Egypt's government in 1882, but nominal allegiance to the Ottoman Empire continued until 1914. Partially independent from the UK in 1922, Egypt acquired full sovereignty with the overthrow of the British-backed monarchy in 1952. The completion of the Aswan High Dam in 1971 and the resultant Lake Nasser have altered the time-honored place of the Nile River in the agriculture and ecology of Egypt. A rapidly growing population (the largest in the Arab world), limited arable land, and dependence on the Nile all continue to overtax resources and stress society. The government has struggled to meet the demands of Egypt's growing population through economic reform and massive investment in communications and physical infrastructure. Egyptian youth and opposition groups, inspired by events in Tunisia leading to overthrow of the government there, organized a "Day of Rage" campaign on 25 January 2011 (Police Day) to include non-violent demonstrations, marches, and labor strikes in Cairo and other cities throughout Egypt. Protester grievances focused on police brutality, state emergency laws, lack of free speech and elections, high unemployment, rising food prices, inflation, and low minimum wages. Within several days of the onset of protests, President MUBARAK addressed the nation pledging the formation of a new government, and in a second address he offered additional concessions, which failed to assuage protesters and resulted in an escalation of the number and intensity of demonstrations and clashes with police. On 11 February MUBARAK resigned and national leadership was assumed by a Supreme Council of Armed Forces (SCAF). The SCAF dissolved the Egyptian parliament, suspended the nation's constitution, and formed a committee to recommend constitutional changes to facilitate a political transition through democratic elections. Following some delays, elections for a new parliament took place between November 2011 and January 2012. Presidential elections held in May and June witnessed the victory of Muslim Brotherhood candidate Mohammed MURSI over former Prime Minister Ahmed SHAFIQ. The regularity and richness of the annual Nile River flood, coupled with semi-isolation provided by deserts to the east and west, allowed for the development of one of the world's great civilizations. A unified kingdom arose circa 3200 B.C., and a series of dynasties ruled in Egypt for the next three millennia. The last native dynasty fell to the Persians in 341 B.C., who in turn were replaced by the Greeks, Romans, and Byzantines. It was the Arabs who introduced Islam and the Arabic language in the 7th century and who ruled for the next six centuries. A local military caste, the Mamluks took control about 1250 and continued to govern after the conquest of Egypt by the Ottoman Turks in 1517. Following the completion of the Suez Canal in 1869, Egypt became an important world transportation hub, but also fell heavily into debt. Ostensibly to protect its investments, Britain seized control of Egypt's government in 1882, but nominal allegiance to the Ottoman Empire continued until 1914. Partially independent from the UK in 1922, Egypt acquired full sovereignty with the overthrow of the British-backed monarchy in 1952. The completion of the Aswan High Dam in 1971 and the resultant Lake Nasser have altered the time-honored place of the Nile River in the agriculture and ecology of Egypt. A rapidly growing population (the largest in the Arab world), limited arable land, and dependence on the Nile all continue to overtax resources and stress society. The government has struggled to meet the demands of Egypt's growing population through economic reform and massive investment in communications and physical infrastructure. Egyptian youth and opposition groups, inspired by events in Tunisia leading to overthrow of the government there, organized a "Day of Rage" campaign on 25 January 2011 (Police Day) to include non-violent demonstrations, marches, and labor strikes in Cairo and other cities throughout Egypt. Protester grievances focused on police brutality, state emergency laws, lack of free speech and elections, high unemployment, rising food prices, inflation, and low minimum wages. Within several days of the onset of protests, President MUBARAK addressed the nation pledging the formation of a new government, and in a second address he offered additional concessions, which failed to assuage protesters and resulted in an escalation of the number and intensity of demonstrations and clashes with police. On 11 February MUBARAK resigned and national leadership was assumed by a Supreme Council of Armed Forces (SCAF). The SCAF dissolved the Egyptian parliament, suspended the nation's constitution, and formed a committee to recommend constitutional changes to facilitate a political transition through democratic elections. Following some delays, elections for a new parliament took place between November 2011 and January 2012. Presidential elections held in May and June witnessed the victory of Muslim Brotherhood candidate Mohammed MURSI over former Prime Minister Ahmed SHAFIQ. |
|
Advertisements
|
Advertisements
|
Airports World Ranking: 67
84 (2012)
Airports - with paved runways
Total 72
Over 3,047 m 15
2,438 to 3,047 m 36
1,524 to 2,437 m 15
Under 914 m 6 (2012)
Airports - with unpaved runways
Total 12
2,438 to 3,047 m 1
1,524 to 2,437 m 3
914 to 1,523 m 5
Under 914 m 3 (2012)
Heliports
6 (2012)
Pipelines
Condensate 320 km; condensate/gas 13 km; gas 6,628 km; liquid petroleum gas 956 km; oil 4,332 km; oil/gas/water 3 km; refined products 895 km; water 13 km (2010)
Railways World Ranking: 34
Total 5,083 km Standard gauge 5,083 km 1.435-m gauge (62 km electrified) (2009)
Roadways World Ranking: 70
Total 65,050 km
Paved 47,500 km
Unpaved 17,550 km (2009)
Waterways World Ranking: 30
3,500 km (includes the Nile River, Lake Nasser, Alexandria-Cairo Waterway, and numerous smaller canals in Nile Delta; the Suez Canal (193.5 km including approaches) is navigable by oceangoing vessels drawing up to 17.68 m) (2011)
Merchant marine World Ranking: 62
Total 67 By type Bulk carrier 16, cargo 20, container 3, passenger/cargo 7, petroleum tanker 12, roll on/roll off 9 Foreign-owned 13 (Denmark 1, France 1, Greece 8, Jordan 2, Lebanon 1) Registered in other countries 42 (Cambodia 4, Georgia 7, Honduras 2, Liberia 3, Malta 1, Marshall Islands 1, Moldova 5, Panama 11, Saint Kitts and Nevis 1, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 2, Saudi Arabia 1, Sierra Leone 3, unknown 1) (2010)
Ports and terminals
Ayn Sukhnah, Alexandria, Damietta, El Dekheila, Port Said, Sidi Kurayr, Suez
--- There are no comments yet ---
Add a new comment:
|
Advertisement
Members area
Egypt (Cairo):
GPS points from Egypt (Cairo)
|



 The regularity and richness of the annual Nile River flood, coupled with semi-isolation provided by deserts to the east and west, allowed for the development of one of the world's great civilizations. A unified kingdom arose circa 3200 B.C., and a series of dynasties ruled in Egypt for the next three millennia. The last native dynasty fell to the Persians in 341 B.C., who in turn were replaced by the Greeks, Romans, and Byzantines. It was the Arabs who introduced Islam and the Arabic language in the 7th century and who ruled for the next six centuries. A local military caste, the Mamluks took control about 1250 and continued to govern after the conquest of Egypt by the Ottoman Turks in 1517. Following the completion of the Suez Canal in 1869, Egypt became an important world transportation hub, but also fell heavily into debt. Ostensibly to protect its investments, Britain seized control of Egypt's government in 1882, but nominal allegiance to the Ottoman Empire continued until 1914. Partially independent from the UK in 1922, Egypt acquired full sovereignty with the overthrow of the British-backed monarchy in 1952. The completion of the Aswan High Dam in 1971 and the resultant Lake Nasser have altered the time-honored place of the Nile River in the agriculture and ecology of Egypt. A rapidly growing population (the largest in the Arab world), limited arable land, and dependence on the Nile all continue to overtax resources and stress society. The government has struggled to meet the demands of Egypt's growing population through economic reform and massive investment in communications and physical infrastructure. Egyptian youth and opposition groups, inspired by events in Tunisia leading to overthrow of the government there, organized a "Day of Rage" campaign on 25 January 2011 (Police Day) to include non-violent demonstrations, marches, and labor strikes in Cairo and other cities throughout Egypt. Protester grievances focused on police brutality, state emergency laws, lack of free speech and elections, high unemployment, rising food prices, inflation, and low minimum wages. Within several days of the onset of protests, President MUBARAK addressed the nation pledging the formation of a new government, and in a second address he offered additional concessions, which failed to assuage protesters and resulted in an escalation of the number and intensity of demonstrations and clashes with police. On 11 February MUBARAK resigned and national leadership was assumed by a Supreme Council of Armed Forces (SCAF). The SCAF dissolved the Egyptian parliament, suspended the nation's constitution, and formed a committee to recommend constitutional changes to facilitate a political transition through democratic elections. Following some delays, elections for a new parliament took place between November 2011 and January 2012. Presidential elections held in May and June witnessed the victory of Muslim Brotherhood candidate Mohammed MURSI over former Prime Minister Ahmed SHAFIQ.
The regularity and richness of the annual Nile River flood, coupled with semi-isolation provided by deserts to the east and west, allowed for the development of one of the world's great civilizations. A unified kingdom arose circa 3200 B.C., and a series of dynasties ruled in Egypt for the next three millennia. The last native dynasty fell to the Persians in 341 B.C., who in turn were replaced by the Greeks, Romans, and Byzantines. It was the Arabs who introduced Islam and the Arabic language in the 7th century and who ruled for the next six centuries. A local military caste, the Mamluks took control about 1250 and continued to govern after the conquest of Egypt by the Ottoman Turks in 1517. Following the completion of the Suez Canal in 1869, Egypt became an important world transportation hub, but also fell heavily into debt. Ostensibly to protect its investments, Britain seized control of Egypt's government in 1882, but nominal allegiance to the Ottoman Empire continued until 1914. Partially independent from the UK in 1922, Egypt acquired full sovereignty with the overthrow of the British-backed monarchy in 1952. The completion of the Aswan High Dam in 1971 and the resultant Lake Nasser have altered the time-honored place of the Nile River in the agriculture and ecology of Egypt. A rapidly growing population (the largest in the Arab world), limited arable land, and dependence on the Nile all continue to overtax resources and stress society. The government has struggled to meet the demands of Egypt's growing population through economic reform and massive investment in communications and physical infrastructure. Egyptian youth and opposition groups, inspired by events in Tunisia leading to overthrow of the government there, organized a "Day of Rage" campaign on 25 January 2011 (Police Day) to include non-violent demonstrations, marches, and labor strikes in Cairo and other cities throughout Egypt. Protester grievances focused on police brutality, state emergency laws, lack of free speech and elections, high unemployment, rising food prices, inflation, and low minimum wages. Within several days of the onset of protests, President MUBARAK addressed the nation pledging the formation of a new government, and in a second address he offered additional concessions, which failed to assuage protesters and resulted in an escalation of the number and intensity of demonstrations and clashes with police. On 11 February MUBARAK resigned and national leadership was assumed by a Supreme Council of Armed Forces (SCAF). The SCAF dissolved the Egyptian parliament, suspended the nation's constitution, and formed a committee to recommend constitutional changes to facilitate a political transition through democratic elections. Following some delays, elections for a new parliament took place between November 2011 and January 2012. Presidential elections held in May and June witnessed the victory of Muslim Brotherhood candidate Mohammed MURSI over former Prime Minister Ahmed SHAFIQ.