|

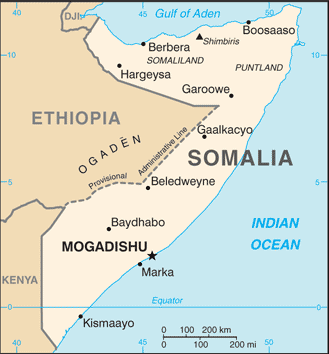
Administrative divisions (GPS Maps)
Geography
People and Society
Government
Economy
Communications
Transportation
Military |
 |
 Britain withdrew from British Somaliland in 1960 to allow its protectorate to join with Italian Somaliland and form the new nation of Somalia. In 1969, a coup headed by Mohamed SIAD Barre ushered in an authoritarian socialist rule characterized by the persecution, jailing and torture of political opponents and dissidents. After the regime's collapse early in 1991, Somalia descended into turmoil, factional fighting, and anarchy. In May 1991, northern clans declared an independent Republic of Somaliland that now includes the administrative regions of Awdal, Woqooyi Galbeed, Togdheer, Sanaag, and Sool. Although not recognized by any government, this entity has maintained a stable existence and continues efforts to establish a constitutional democracy, including holding municipal, parliamentary, and presidential elections. The regions of Bari, Nugaal, and northern Mudug comprise a neighboring semi-autonomous state of Puntland, which has been self-governing since 1998 but does not aim at independence; it has also made strides toward reconstructing a legitimate, representative government but has suffered some civil strife. Puntland disputes its border with Somaliland as it also claims portions of eastern Sool and Sanaag. Beginning in 1993, a two-year UN humanitarian effort (primarily in the south) was able to alleviate famine conditions, but when the UN withdrew in 1995, having suffered significant casualties, order still had not been restored. In 2000, the Somalia National Peace Conference (SNPC) held in Djibouti resulted in the formation of an interim government, known as the Transitional National Government (TNG). When the TNG failed to establish adequate security or governing institutions, the Government of Kenya, under the auspices of the Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD), led a subsequent peace process that concluded in October 2004 with the election of Abdullahi YUSUF Ahmed as President of a second interim government, known as the Transitional Federal Government (TFG) of the Somali Republic. The TFG included a 275-member parliamentary body, known as the Transitional Federal Parliament (TFP). President YUSUF resigned late in 2008 while United Nations-sponsored talks between the TFG and the opposition Alliance for the Re-Liberation of Somalia (ARS) were underway in Djibouti. In January 2009, following the creation of a TFG-ARS unity government, Ethiopian military forces, which had entered Somalia in December 2006 to support the TFG in the face of advances by the opposition Islamic Courts Union (ICU), withdrew from the country. The TFP was doubled in size to 550 seats with the addition of 200 ARS and 75 civil society members of parliament. The expanded parliament elected Sheikh SHARIF Sheikh Ahmed, the former ICU and ARS chairman as president in January 2009. The creation of the TFG was based on the Transitional Federal Charter (TFC), which outlined a five-year mandate leading to the establishment of a new Somali constitution and a transition to a representative government following national elections. In 2009, the TFP amended the TFC to extend TFG's mandate until 2011 and in 2011 Somali principals agreed to institute political transition by August 2012. The transition process ended in September 2012 when clan elders appointed 275 members to a new parliament replacing the TFP and the subsequent election, by parliament, of a new president. Britain withdrew from British Somaliland in 1960 to allow its protectorate to join with Italian Somaliland and form the new nation of Somalia. In 1969, a coup headed by Mohamed SIAD Barre ushered in an authoritarian socialist rule characterized by the persecution, jailing and torture of political opponents and dissidents. After the regime's collapse early in 1991, Somalia descended into turmoil, factional fighting, and anarchy. In May 1991, northern clans declared an independent Republic of Somaliland that now includes the administrative regions of Awdal, Woqooyi Galbeed, Togdheer, Sanaag, and Sool. Although not recognized by any government, this entity has maintained a stable existence and continues efforts to establish a constitutional democracy, including holding municipal, parliamentary, and presidential elections. The regions of Bari, Nugaal, and northern Mudug comprise a neighboring semi-autonomous state of Puntland, which has been self-governing since 1998 but does not aim at independence; it has also made strides toward reconstructing a legitimate, representative government but has suffered some civil strife. Puntland disputes its border with Somaliland as it also claims portions of eastern Sool and Sanaag. Beginning in 1993, a two-year UN humanitarian effort (primarily in the south) was able to alleviate famine conditions, but when the UN withdrew in 1995, having suffered significant casualties, order still had not been restored. In 2000, the Somalia National Peace Conference (SNPC) held in Djibouti resulted in the formation of an interim government, known as the Transitional National Government (TNG). When the TNG failed to establish adequate security or governing institutions, the Government of Kenya, under the auspices of the Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD), led a subsequent peace process that concluded in October 2004 with the election of Abdullahi YUSUF Ahmed as President of a second interim government, known as the Transitional Federal Government (TFG) of the Somali Republic. The TFG included a 275-member parliamentary body, known as the Transitional Federal Parliament (TFP). President YUSUF resigned late in 2008 while United Nations-sponsored talks between the TFG and the opposition Alliance for the Re-Liberation of Somalia (ARS) were underway in Djibouti. In January 2009, following the creation of a TFG-ARS unity government, Ethiopian military forces, which had entered Somalia in December 2006 to support the TFG in the face of advances by the opposition Islamic Courts Union (ICU), withdrew from the country. The TFP was doubled in size to 550 seats with the addition of 200 ARS and 75 civil society members of parliament. The expanded parliament elected Sheikh SHARIF Sheikh Ahmed, the former ICU and ARS chairman as president in January 2009. The creation of the TFG was based on the Transitional Federal Charter (TFC), which outlined a five-year mandate leading to the establishment of a new Somali constitution and a transition to a representative government following national elections. In 2009, the TFP amended the TFC to extend TFG's mandate until 2011 and in 2011 Somali principals agreed to institute political transition by August 2012. The transition process ended in September 2012 when clan elders appointed 275 members to a new parliament replacing the TFP and the subsequent election, by parliament, of a new president. |
|
Advertisements
|
Advertisements
|
Airports World Ranking: 80
62 (2012)
Airports - with paved runways
Total 7
Over 3,047 m 4
2,438 to 3,047 m 2
1,524 to 2,437 m 1 (2012)
Airports - with unpaved runways
Total 55
Over 3,047 m 1
2,438 to 3,047 m 4
1,524 to 2,437 m 20
914 to 1,523 m 24
Under 914 m 6 (2012)
Roadways World Ranking: 108
Total 22,100 km
Paved 2,608 km
Unpaved 19,492 km (2000)
Merchant marine World Ranking: 155
Total 1
By type Cargo 1 (2008)
Ports and terminals
Berbera, Kismaayo
Transportation - note
The International Maritime Bureau reports the territorial and offshore waters in the Gulf of Aden and Indian Ocean remain the region of greatest risk for piracy and armed robbery against ships accounting for 50% of all attacks in 2010; 217 vessels, including commercial shipping and pleasure craft, were attacked or hijacked both at anchor and while underway; hijackings off the coast of Somalia accounted for 92% of all ship seizures in 2010; as of May 2011, 26 vessels and 522 hostages were being held for ransom by Somali pirates; the presence of several naval task forces in the Gulf of Aden and additional anti-piracy measures on the part of ship operators have reduced piracy incidents in that body of water; in response Somali-based pirates, using hijacked fishing trawlers as "mother ships" to extend their range, shifted operations as far south as the Mozambique Channel and eastward to the vicinity of the Maldives
--- There are no comments yet ---
Add a new comment:
|
Advertisement
Members area
Somalia (Mogadishu):
GPS points from Somalia (Mogadishu)
|



 Britain withdrew from British Somaliland in 1960 to allow its protectorate to join with Italian Somaliland and form the new nation of Somalia. In 1969, a coup headed by Mohamed SIAD Barre ushered in an authoritarian socialist rule characterized by the persecution, jailing and torture of political opponents and dissidents. After the regime's collapse early in 1991, Somalia descended into turmoil, factional fighting, and anarchy. In May 1991, northern clans declared an independent Republic of Somaliland that now includes the administrative regions of Awdal, Woqooyi Galbeed, Togdheer, Sanaag, and Sool. Although not recognized by any government, this entity has maintained a stable existence and continues efforts to establish a constitutional democracy, including holding municipal, parliamentary, and presidential elections. The regions of Bari, Nugaal, and northern Mudug comprise a neighboring semi-autonomous state of Puntland, which has been self-governing since 1998 but does not aim at independence; it has also made strides toward reconstructing a legitimate, representative government but has suffered some civil strife. Puntland disputes its border with Somaliland as it also claims portions of eastern Sool and Sanaag. Beginning in 1993, a two-year UN humanitarian effort (primarily in the south) was able to alleviate famine conditions, but when the UN withdrew in 1995, having suffered significant casualties, order still had not been restored. In 2000, the Somalia National Peace Conference (SNPC) held in Djibouti resulted in the formation of an interim government, known as the Transitional National Government (TNG). When the TNG failed to establish adequate security or governing institutions, the Government of Kenya, under the auspices of the Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD), led a subsequent peace process that concluded in October 2004 with the election of Abdullahi YUSUF Ahmed as President of a second interim government, known as the Transitional Federal Government (TFG) of the Somali Republic. The TFG included a 275-member parliamentary body, known as the Transitional Federal Parliament (TFP). President YUSUF resigned late in 2008 while United Nations-sponsored talks between the TFG and the opposition Alliance for the Re-Liberation of Somalia (ARS) were underway in Djibouti. In January 2009, following the creation of a TFG-ARS unity government, Ethiopian military forces, which had entered Somalia in December 2006 to support the TFG in the face of advances by the opposition Islamic Courts Union (ICU), withdrew from the country. The TFP was doubled in size to 550 seats with the addition of 200 ARS and 75 civil society members of parliament. The expanded parliament elected Sheikh SHARIF Sheikh Ahmed, the former ICU and ARS chairman as president in January 2009. The creation of the TFG was based on the Transitional Federal Charter (TFC), which outlined a five-year mandate leading to the establishment of a new Somali constitution and a transition to a representative government following national elections. In 2009, the TFP amended the TFC to extend TFG's mandate until 2011 and in 2011 Somali principals agreed to institute political transition by August 2012. The transition process ended in September 2012 when clan elders appointed 275 members to a new parliament replacing the TFP and the subsequent election, by parliament, of a new president.
Britain withdrew from British Somaliland in 1960 to allow its protectorate to join with Italian Somaliland and form the new nation of Somalia. In 1969, a coup headed by Mohamed SIAD Barre ushered in an authoritarian socialist rule characterized by the persecution, jailing and torture of political opponents and dissidents. After the regime's collapse early in 1991, Somalia descended into turmoil, factional fighting, and anarchy. In May 1991, northern clans declared an independent Republic of Somaliland that now includes the administrative regions of Awdal, Woqooyi Galbeed, Togdheer, Sanaag, and Sool. Although not recognized by any government, this entity has maintained a stable existence and continues efforts to establish a constitutional democracy, including holding municipal, parliamentary, and presidential elections. The regions of Bari, Nugaal, and northern Mudug comprise a neighboring semi-autonomous state of Puntland, which has been self-governing since 1998 but does not aim at independence; it has also made strides toward reconstructing a legitimate, representative government but has suffered some civil strife. Puntland disputes its border with Somaliland as it also claims portions of eastern Sool and Sanaag. Beginning in 1993, a two-year UN humanitarian effort (primarily in the south) was able to alleviate famine conditions, but when the UN withdrew in 1995, having suffered significant casualties, order still had not been restored. In 2000, the Somalia National Peace Conference (SNPC) held in Djibouti resulted in the formation of an interim government, known as the Transitional National Government (TNG). When the TNG failed to establish adequate security or governing institutions, the Government of Kenya, under the auspices of the Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD), led a subsequent peace process that concluded in October 2004 with the election of Abdullahi YUSUF Ahmed as President of a second interim government, known as the Transitional Federal Government (TFG) of the Somali Republic. The TFG included a 275-member parliamentary body, known as the Transitional Federal Parliament (TFP). President YUSUF resigned late in 2008 while United Nations-sponsored talks between the TFG and the opposition Alliance for the Re-Liberation of Somalia (ARS) were underway in Djibouti. In January 2009, following the creation of a TFG-ARS unity government, Ethiopian military forces, which had entered Somalia in December 2006 to support the TFG in the face of advances by the opposition Islamic Courts Union (ICU), withdrew from the country. The TFP was doubled in size to 550 seats with the addition of 200 ARS and 75 civil society members of parliament. The expanded parliament elected Sheikh SHARIF Sheikh Ahmed, the former ICU and ARS chairman as president in January 2009. The creation of the TFG was based on the Transitional Federal Charter (TFC), which outlined a five-year mandate leading to the establishment of a new Somali constitution and a transition to a representative government following national elections. In 2009, the TFP amended the TFC to extend TFG's mandate until 2011 and in 2011 Somali principals agreed to institute political transition by August 2012. The transition process ended in September 2012 when clan elders appointed 275 members to a new parliament replacing the TFP and the subsequent election, by parliament, of a new president.