
|
|
Advertisements:
EconomyEconomy - overview
North Korea, one of the world's most centrally directed and least open economies, faces chronic economic problems. Industrial capital stock is nearly beyond repair as a result of years of underinvestment, shortages of spare parts, and poor maintenance. Large-scale military spending draws off resources needed for investment and civilian consumption. Industrial and power output have stagnated for years at a fraction of pre-1990 levels. Frequent weather-related crop failures aggravated chronic food shortages caused by on-going systemic problems, including a lack of arable land, collective farming practices, poor soil quality, insufficient fertilization, and persistent shortages of tractors and fuel. Large-scale international food aid deliveries have allowed the people of North Korea to escape widespread starvation since famine threatened in 1995, but the population continues to suffer from prolonged malnutrition and poor living conditions. Since 2002, the government has allowed private "farmers' markets" to begin selling a wider range of goods. It also permitted some private farming - on an experimental basis - in an effort to boost agricultural output. In December 2009, North Korea carried out a redenomination of its currency, capping the amount of North Korean won that could be exchanged for the new notes, and limiting the exchange to a one-week window. A concurrent crackdown on markets and foreign currency use yielded severe shortages and inflation, forcing Pyongyang to ease the restrictions by February 2010. In response to the sinking of the South Korean destroyer Cheonan and the shelling of Yeonpyeong Island, South Korea's government cut off most aid, trade, and bilateral cooperation activities, with the exception of operations at the Kaesong Industrial Complex. In preparation for 2012, the 100th anniversary of KIM Il-sung's birthday, North Korea continued efforts to develop special economic zones with China and expressed willingness to permit construction of a trilateral gas pipeline that would carry Russian natural gas to South Korea. The North Korean government often highlights its 2012 goal of becoming a "strong and prosperous" nation and attracting foreign investment, a key factor for improving the overall standard of living. Nevertheless, firm political control remains the government's overriding concern, which likely will inhibit changes to North Korea's current economic system. Gdp (purchasing power parity) World Ranking: 99
$40 billion (2011 est.)
$40 billion (2010 est.) $40 billion (2009 est.) Note Data are in 2011 US dollars; North Korea does not publish reliable National Income Accounts data; the data shown here are derived from purchasing power parity (PPP) GDP estimates for North Korea that were made by Angus MADDISON in a study conducted for the OECD; his figure for 1999 was extrapolated to 2011 using estimated real growth rates for North Korea's GDP and an inflation factor based on the US GDP deflator; the results were rounded to the nearest $10 billion. Gdp (official exchange rate)
$28 billion (2009 est.)
Gdp - real growth rate World Ranking: 96
4% (2011 est.)
-0.4% (2010 est.) -0.9% (2009 est.) Gdp - per capita (ppp) World Ranking: 194
$1,800 (2011 est.)
$1,800 (2010 est.) $1,900 (2009 est.) Note Data are in 2011 US dollars Gdp - composition by sector
Agriculture 23%
Industry 43.4% Services 33.6% (2011 est.) Labor force World Ranking: 42
12.2 million
Note Estimates vary widely (2009 est.) Labor force - by occupation
Agriculture 35%
Industry and services 65% (2008 est.) Unemployment rate
NA%
Population below poverty line
NA%
Household income or consumption by percentage share
Lowest 10% NA%
Highest 10% NA% Budget
Revenues $3.2 billion
Expenditures $3.3 billion (2007 est.) Taxes and other revenues World Ranking: 207
11.4% of GDP
Note Excludes earnings from state-operated enterprises (2007 est.) Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-) World Ranking: 51
-0.4% of GDP (2007 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
NA%
Agriculture - products
Rice, corn, potatoes, soybeans, pulses; cattle, pigs, pork, eggs Industries
Military products; machine building, electric power, chemicals; mining (coal, iron ore, limestone, magnesite, graphite, copper, zinc, lead, and precious metals), metallurgy; textiles, food processing; tourism Industrial production growth rate
NA%
Electricity - production World Ranking: 68
22.52 billion kWh (2008 est.)
Electricity - consumption World Ranking: 70
18.85 billion kWh (2008 est.)
Electricity - exports
0 kWh (2009 est.)
Electricity - imports
0 kWh (2009 est.)
Oil - production World Ranking: 117
118 bbl/day (2010 est.)
Oil - consumption World Ranking: 145
13,000 bbl/day (2010 est.)
Oil - exports World Ranking: 168
0 bbl/day (2009 est.)
Oil - imports World Ranking: 124
15,810 bbl/day (2009 est.)
Oil - proved reserves World Ranking: 149
0 bbl (1 January 2011 est.)
Natural gas - production World Ranking: 199
0 cu m (2009 est.)
Natural gas - consumption World Ranking: 193
0 cu m (2009 est.)
Natural gas - exports World Ranking: 125
0 cu m (2009 est.)
Natural gas - imports World Ranking: 83
0 cu m (2009 est.)
Natural gas - proved reserves World Ranking: 193
0 cu m (1 January 2011 est.)
Exports World Ranking: 132
$2.557 billion (2010)
$2.554 billion (2010 est.) Exports - commodities
Minerals, metallurgical products, manufactures (including armaments), textiles, agricultural and fishery products Exports - partners
China 46.5%, South Korea 40.8%, Bangladesh 1.4% (2010 est.) Imports World Ranking: 138
$3.528 billion (2010 est.)
$3.096 billion (2009) Imports - commodities
Petroleum, coking coal, machinery and equipment, textiles, grain Imports - partners
China 64.5%, South Korea 24.6%, Russia 2.4% (2010 est.) Debt - external World Ranking: 89
$12.5 billion (2001 est.)
Exchange rates
North Korean won (KPW) per US dollar (market rate) 145 (2011)145 (2010 est.) 3,630 (December 2008) 140 (2007) Fiscal year
Calendar year
Comments
Add a new comment: |
Advertisement
Members area
North Korea (Pyongyang):
GPS points from North Korea (Pyongyang)
|
||||||||
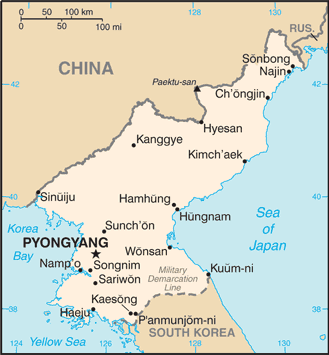
 An independent kingdom for much of its long history, Korea was occupied by Japan beginning in 1905 following the Russo-Japanese War. Five years later, Japan formally annexed the entire peninsula. Following World War II, Korea was split with the northern half coming under Soviet-sponsored Communist control. After failing in the Korean War (1950-53) to conquer the US-backed Republic of Korea (ROK) in the southern portion by force, North Korea (DPRK), under its founder President KIM Il Sung, adopted a policy of ostensible diplomatic and economic "self-reliance" as a check against outside influence. The DPRK demonized the US as the ultimate threat to its social system through state-funded propaganda, and molded political, economic, and military policies around the core ideological objective of eventual unification of Korea under Pyongyang's control. KIM Il Sung's son, KIM Jong Il, was officially designated as his father's successor in 1980, assuming a growing political and managerial role until the elder KIM's death in 1994. KIM Jong Un was publicly unveiled as his father's successor in September 2010. Following KIM Jong Il's death in December 2011, the regime began to take actions to transfer power to KIM Jong Un and Jong Un has begun to assume his father's former titles and duties. After decades of economic mismanagement and resource misallocation, the DPRK since the mid-1990s has relied heavily on international aid to feed its population. North Korea's history of regional military provocations, proliferation of military-related items, long-range missile development, WMD programs including tests of nuclear devices in 2006 and 2009, and massive conventional armed forces are of major concern to the international community. The regime has marked 2012, the centenary of KIM Il Sung's birth, a banner year; to that end, the country has heightened its focus on developing its economy and improving its people's livelihoods.
An independent kingdom for much of its long history, Korea was occupied by Japan beginning in 1905 following the Russo-Japanese War. Five years later, Japan formally annexed the entire peninsula. Following World War II, Korea was split with the northern half coming under Soviet-sponsored Communist control. After failing in the Korean War (1950-53) to conquer the US-backed Republic of Korea (ROK) in the southern portion by force, North Korea (DPRK), under its founder President KIM Il Sung, adopted a policy of ostensible diplomatic and economic "self-reliance" as a check against outside influence. The DPRK demonized the US as the ultimate threat to its social system through state-funded propaganda, and molded political, economic, and military policies around the core ideological objective of eventual unification of Korea under Pyongyang's control. KIM Il Sung's son, KIM Jong Il, was officially designated as his father's successor in 1980, assuming a growing political and managerial role until the elder KIM's death in 1994. KIM Jong Un was publicly unveiled as his father's successor in September 2010. Following KIM Jong Il's death in December 2011, the regime began to take actions to transfer power to KIM Jong Un and Jong Un has begun to assume his father's former titles and duties. After decades of economic mismanagement and resource misallocation, the DPRK since the mid-1990s has relied heavily on international aid to feed its population. North Korea's history of regional military provocations, proliferation of military-related items, long-range missile development, WMD programs including tests of nuclear devices in 2006 and 2009, and massive conventional armed forces are of major concern to the international community. The regime has marked 2012, the centenary of KIM Il Sung's birth, a banner year; to that end, the country has heightened its focus on developing its economy and improving its people's livelihoods. 