
|
|
Advertisements:
GeographyLocation
Southern South America, bordering the South Atlantic Ocean, between Chile and Uruguay Geographic coordinates
34 00 S, 64 00 W
Map references
South America
Area World Ranking: 8
Total 2,780,400 sq km
Land 2,736,690 sq km Water 43,710 sq km Area - comparative
Slightly less than three-tenths the size of the US Land boundaries
Total 9,861 km
Border countries Bolivia 832 km, Brazil 1,261 km, Chile 5,308 km, Paraguay 1,880 km, Uruguay 580 km Coastline
4,989 km
Maritime claims
Territorial sea 12 nm
Contiguous zone 24 nm Exclusive economic zone 200 nm Continental shelf 200 nm or to the edge of the continental margin Climate
Mostly temperate; arid in southeast; subantarctic in southwest Terrain
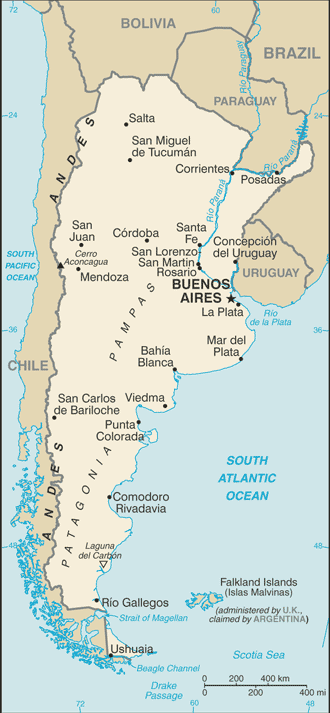
Rich plains of the Pampas in northern half, flat to rolling plateau of Patagonia in south, rugged Andes along western border Elevation extremes
Lowest point
Laguna del Carbon -105 m (located between Puerto San Julian and Comandante Luis Piedra Buena in the province of Santa Cruz) Highest point Cerro Aconcagua 6,960 m (located in the northwestern corner of the province of Mendoza) Natural resources
Fertile plains of the pampas, lead, zinc, tin, copper, iron ore, manganese, petroleum, uranium Land use
Arable land 10.03%
Permanent crops 0.36% Other 89.61% (2005) Irrigated land
15,500 sq km (2003)
Total renewable water resources
814 cu km (2000)
Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural)
Total 29.19 cu km/yr (17%/9%/74%)
Per capita 753 cu m/yr (2000) Natural hazards
San Miguel de Tucuman and Mendoza areas in the Andes subject to earthquakes; pamperos are violent windstorms that can strike the pampas and northeast; heavy flooding in some areas Volcanism Volcanic activity in the Andes Mountains along the Chilean border; Copahue (elev. 2,997 m) last erupted in 2000; other historically active volcanoes include Llullaillaco, Maipo, Planchon-Peteroa, San Jose, Tromen, Tupungatito, and Viedma Environment - current issues
Environmental problems (urban and rural) typical of an industrializing economy such as deforestation, soil degradation, desertification, air pollution, and water pollution Note Argentina is a world leader in setting voluntary greenhouse gas targets Environment - international agreements
Party to
Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling Signed, but not ratified Marine Life ConservationGeography - note
Second-largest country in South America (after Brazil); strategic location relative to sea lanes between the South Atlantic and the South Pacific Oceans (Strait of Magellan, Beagle Channel, Drake Passage); diverse geophysical landscapes range from tropical climates in the north to tundra in the far south; Cerro Aconcagua is the Western Hemisphere's tallest mountain, while Laguna del Carbon is the lowest point in the Western Hemisphere
Comments
Add a new comment: |
Advertisement
Members area
Argentina (Buenos Aires):
GPS points from Argentina (Buenos Aires)
|
||||||||
 In 1816, the United Provinces of the Rio Plata declared their independence from Spain. After Bolivia, Paraguay, and Uruguay went their separate ways, the area that remained became Argentina. The country's population and culture were heavily shaped by immigrants from throughout Europe, but most particularly Italy and Spain, which provided the largest percentage of newcomers from 1860 to 1930. Up until about the mid-20th century, much of Argentina's history was dominated by periods of internal political conflict between Federalists and Unitarians and between civilian and military factions. After World War II, an era of Peronist populism and direct and indirect military interference in subsequent governments was followed by a military junta that took power in 1976. Democracy returned in 1983 after a failed bid to seize the Falkland Islands (Islas Malvinas) by force, and has persisted despite numerous challenges, the most formidable of which was a severe economic crisis in 2001-02 that led to violent public protests and the successive resignations of several presidents.
In 1816, the United Provinces of the Rio Plata declared their independence from Spain. After Bolivia, Paraguay, and Uruguay went their separate ways, the area that remained became Argentina. The country's population and culture were heavily shaped by immigrants from throughout Europe, but most particularly Italy and Spain, which provided the largest percentage of newcomers from 1860 to 1930. Up until about the mid-20th century, much of Argentina's history was dominated by periods of internal political conflict between Federalists and Unitarians and between civilian and military factions. After World War II, an era of Peronist populism and direct and indirect military interference in subsequent governments was followed by a military junta that took power in 1976. Democracy returned in 1983 after a failed bid to seize the Falkland Islands (Islas Malvinas) by force, and has persisted despite numerous challenges, the most formidable of which was a severe economic crisis in 2001-02 that led to violent public protests and the successive resignations of several presidents.