
|
|
Advertisements:
GovernmentCountry name
Conventional long form None
Conventional short form Malaysia Local long form None Local short form Malaysia Former Federation of Malaya Government type
Constitutional monarchy
Note Nominally headed by paramount ruler (commonly referred to as the King) and a bicameral Parliament consisting of a nonelected upper house and an elected lower house; all Peninsular Malaysian states have hereditary rulers (commonly referred to as sultans) except Melaka and Pulau Pinang (Penang); those two states along with Sabah and Sarawak in East Malaysia have governors appointed by government; powers of state governments are limited by federal constitution; under terms of federation, Sabah and Sarawak retain certain constitutional prerogatives (e.g., right to maintain their own immigration controls) Capital
Name Kuala Lumpur
Geographic coordinates 3 10 N, 101 42 E Time difference UTC+8 (13 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time) Note Putrajaya is referred to as an administrative center not the capital; Parliament meets in Kuala Lumpur Administrative divisions
13 states (negeri-negeri, singular - negeri) Johor, Kedah, Kelantan, Melaka, Negeri Sembilan, Pahang, Perak, Perlis, Pulau Pinang, Sabah, Sarawak, Selangor, Terengganu; and 1 federal territory (Wilayah Persekutuan) with three components, city of Kuala Lumpur, Labuan, and Putrajaya Independence
31 August 1957 (from the UK)
National holiday
Independence Day 31 August (1957) (independence of Malaya); Malaysia Day 16 September (1963) (formation of Malaysia) Constitution
31 August 1957; amended many times Legal system
Mixed legal system of English common law, Islamic law, and customary law; judicial review of legislative acts in the Supreme Court at request of supreme head of the federation International law organization participation
Has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt Suffrage
21 years of age; universal
Executive branch
Chief of state
King - Tuanku ABDUL HALIM Mu'adzam Shah (selected on 13 December 2011; installed on 11 April 2012); the position of the king is primarily ceremonial Head of government Prime Minister NAJIB Razak (since 3 April 2009); Deputy Prime Minister MUHYIDDIN bin Mohamed Yassin (since 9 April 2009) Cabinet Cabinet appointed by the prime minister from among the members of Parliament with consent of the king Elections Kings are elected by and from the hereditary rulers of nine of the states for five-year terms; selection is based on the principle of rotation among rulers of states; elections were last held on 14 October 2011 (next to be held in 2016); prime ministers are designated from among the members of the House of Representatives; following legislative elections, the leader who commands the support of the majority of members in the House becomes prime minister (since independence this has been the leader of the UMNO party) Election results Tuanku Abdul HALIM Mu'adzam Shah elected king; Mohamed NAJIB bin Abdul Razak was sworn in as Prime Minister after winning a party election for the presidency of the United Malays National Organization (UMNO), the party that leads the coalition with a majority of seats in parliament Legislative branch
Bicameral Parliament or Parlimen consists of Senate or Dewan Negara (70 seats; 44 members appointed by the king, 26 elected by 13 state legislatures to serve three-year terms with a two term limit) and House of Representatives or Dewan Rakyat (222 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve up to five-year terms) Elections House of Representatives - last held on 8 March 2008 (next to be held by June 2013) Election results House of Representatives - percent of vote - BN coalition 50.3%, opposition parties 46.8%, others 2.9%; seats - BN coalition 140, opposition parties 82; (seats by party as of March 2011 - BN coalition 137, opposition parties 76, independents 9) Judicial branch
Civil courts include Federal Court, Court of Appeal, High Court of Malaya on peninsula Malaysia, and High Court of Sabah and Sarawak in states of Borneo (judges are appointed by the king on the advice of the prime minister); sharia courts include Sharia Appeal Court, Sharia High Court, and Sharia Subordinate Courts at state-level and deal with religious and family matters such as custody, divorce, and inheritance only for Muslims; decisions of sharia courts cannot be appealed to civil courts Political parties and leaders
National Front (Barisan Nasional) or BN (ruling coalition) consists of the following parties
Gerakan Rakyat Malaysia Party or GERAKAN [KOH Tsu Koon]; Liberal Democratic Party (Parti Liberal Demokratik - Sabah) or LDP [LIEW Vui Keong]; Malaysian Chinese Association (Persatuan China Malaysia) or MCA [CHUA Soi Lek]; Malaysian Indian Congress (Kongres India Malaysia) or MIC [Govindasamy PALANIVEL]; Parti Bersatu Rakyat Sabah or PBRS [Joseph KURUP]; Parti Bersatu Sabah or PBS [Joseph PAIRIN Kitingan]; Parti Pesaka Bumiputera Bersatu or PBB [Abdul TAIB Mahmud]; Parti Rakyat Sarawak or PRS [James MASING]; Sarawak United People's Party (Parti Bersatu Rakyat Sarawak) or SUPP [Peter CHIN Fah Kui]; United Malays National Organization or UMNO [NAJIB bin Abdul Razak]; United Pasokmomogun Kadazandusun Murut Organization (Pertubuhan Pasko Momogun Kadazan Dusun Bersatu) or UPKO [Bernard DOMPOK]; People's Progressive Party (Parti Progresif Penduduk Malaysia) or PPP [M.Kayveas]; Sarawak Progressive Democratic Party or SPDP [William MAWAN]) People's Alliance (Pakatan Rakyat) or PR (opposition coalition) consists of the following parties Democratic Action Party (Parti Tindakan Demokratik) or DAP [KARPAL Singh]; Islamic Party of Malaysia (Parti Islam se Malaysia) or PAS [Abdul HADI Awang]; People's Justice Party (Parti Keadilan Rakyat) or PKR [WAN AZIZAH Wan Ismail]; Sarawak National Party or SNAP [Edwin DUNDANG] Independent party Sabah Progressive Party (Parti Progresif Sabah) or SAPP [YONG Teck Lee] Political pressure groups and leaders
Bar Council; BERSIH (electoral reform coalition); PEMBELA (Muslim NGO coalition); PERKASA (defense of Malay rights) Other Religious groups; women's groups; youth groups International organization participation
ADB, APEC, ARF, ASEAN, BIS, C, CICA (observer), CP, D-8, EAS, FAO, G-15, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, MINURSO, MONUSCO, NAM, OIC, OPCW, PCA, PIF (partner), UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNMIT, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO Diplomatic representation in the us
Chief of mission Ambassador OTHMAN Bin Hashim
Chancery 3516 International Court NW, Washington, DC 20008 Telephone [1] (202) 572-9700FAX [1] (202) 572-9882 Consulate(s) general Los Angeles, New York Diplomatic representation from the us
Chief of mission Ambassador Paul W. JONES
Embassy 376 Jalan Tun Razak, 50400 Kuala Lumpur Mailing address US Embassy Kuala Lumpur, APO AP 96535-8152 Telephone [60] (3) 2168-5000FAX [60] (3) 2142-2207 Flag description
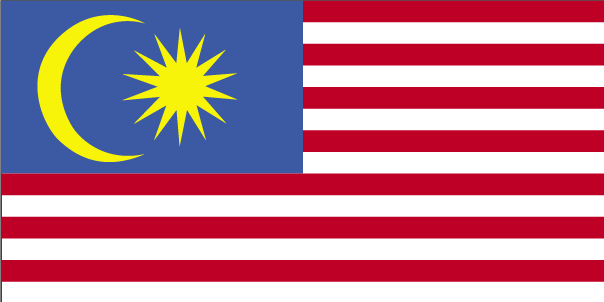
14 equal horizontal stripes of red (top) alternating with white (bottom); there is a blue rectangle in the upper hoist-side corner bearing a yellow crescent and a yellow 14-pointed star; the flag is often referred to as Jalur Gemilang (Stripes of Glory); the 14 stripes stand for the equal status in the federation of the 13 member states and the federal government; the 14 points on the star represent the unity between these entities; the crescent is a traditional symbol of Islam; blue symbolizes the unity of the Malay people and yellow is the royal color of Malay rulers Note The design is based on the flag of the US National symbol(s)
Tiger
National anthem
Name "Negaraku" (My Country)
Lyrics/music Collective, led by Tunku ABDUL RAHMAN/Pierre Jean DE BERANGER Note Adopted 1957; the full version is only performed in the presence of the king; the tune, which was adopted from a popular French melody titled "La Rosalie," was originally the anthem of the state of Perak
Comments
Add a new comment: |
Advertisement
Members area
Malaysia (Kuala Lumpur):
GPS points from Malaysia (Kuala Lumpur)
|
||||||||
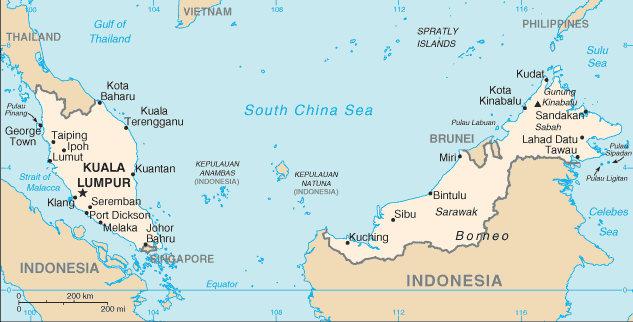
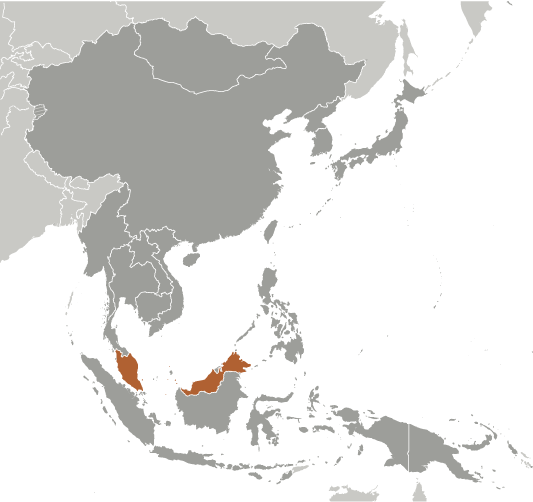
 During the late 18th and 19th centuries, Great Britain established colonies and protectorates in the area of current Malaysia; these were occupied by Japan from 1942 to 1945. In 1948, the British-ruled territories on the Malay Peninsula except Singapore formed the Federation of Malaya, which became independent in 1957. Malaysia was formed in 1963 when the former British colonies of Singapore as well as Sabah and Sarawak on the northern coast of Borneo joined the Federation. The first several years of the country's independence were marred by a Communist insurgency, Indonesian confrontation with Malaysia, Philippine claims to Sabah, and Singapore's departure from the Federation in 1965. During the 22-year term of Prime Minister MAHATHIR bin Mohamad (1981-2003), Malaysia was successful in diversifying its economy from dependence on exports of raw materials to the development of manufacturing, services, and tourism. Prime Minister Mohamed NAJIB bin Abdul Razak (in office since April 2009) has continued these pro-business policies.
During the late 18th and 19th centuries, Great Britain established colonies and protectorates in the area of current Malaysia; these were occupied by Japan from 1942 to 1945. In 1948, the British-ruled territories on the Malay Peninsula except Singapore formed the Federation of Malaya, which became independent in 1957. Malaysia was formed in 1963 when the former British colonies of Singapore as well as Sabah and Sarawak on the northern coast of Borneo joined the Federation. The first several years of the country's independence were marred by a Communist insurgency, Indonesian confrontation with Malaysia, Philippine claims to Sabah, and Singapore's departure from the Federation in 1965. During the 22-year term of Prime Minister MAHATHIR bin Mohamad (1981-2003), Malaysia was successful in diversifying its economy from dependence on exports of raw materials to the development of manufacturing, services, and tourism. Prime Minister Mohamed NAJIB bin Abdul Razak (in office since April 2009) has continued these pro-business policies.